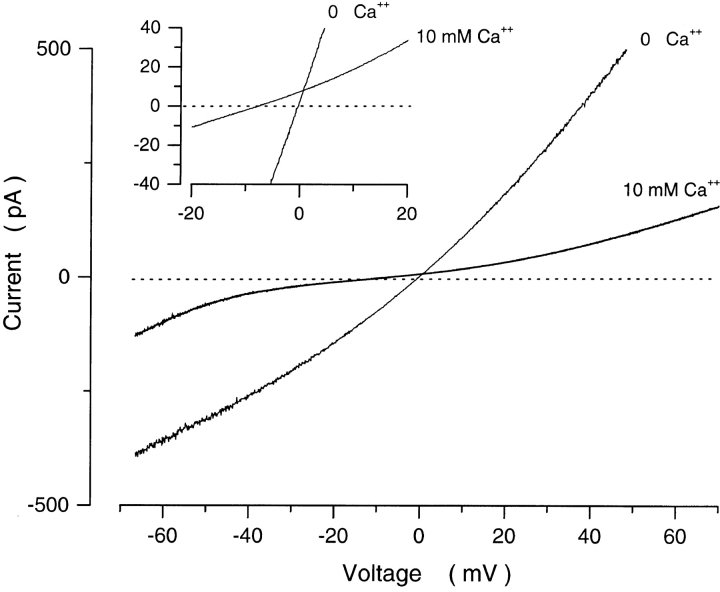
Figure 1.
Effect of cytoplasmic Ca2+ on the I–V curve of cGMP-dependent currents measured in an inside out membrane patch detached from a tiger salamander rod outer segments. Currents were activated with a voltage ramp from −70 to +70 mV in the presence of 300 μM cGMP. Shown are currents measured in the same patch under symmetric Na+ solutions (150 mM) before (0 Ca2+) and after addition of 10 mM Ca2+. The inset illustrates the same data at higher resolution. Addition of Ca2+ blocked the current in a voltage-dependent manner and shifted the zero current potential to a more negative value (−7.3 mV), indicating that Ca2+ is more permeable than Na+ and PCa/PNa = 7.8. The currents shown are corrected for the leak current measured under the same ionic conditions, but in the absence of cGMP.