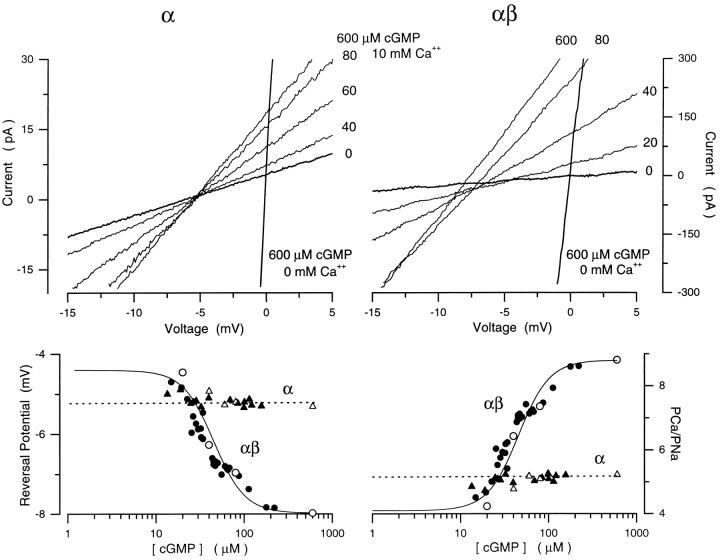
Figure 10.
Ca2+ selectivity as a function of cGMP in recombinant bovine rod α or αβ cGMP-gated channels. I–V curves measured in Xenopus oocyte membranes expressing either homomeric α (top left) or heteromeric αβ (top right) channels. Currents were activated with step concentrations of cGMP in the presence of symmetric Na+ (150 mM) solutions with Ca2+ (10 mM) added to the cytoplasmic side of membrane. cGMP concentrations are given next to each curve. Each trace is the signal average of 10 individual curves measured at each cGMP concentration. Also shown are I–V curves measured under symmetric Na+ in the absence of cGMP or after addition of saturating cGMP (600 μM) in order to define the origin (0,0) of the I–V plane. (Bottom left) Reversal potentials as a function of [cGMP] measured in α (▴) or αβ (•)channels. Open symbols are data measured in the same patch with steps of cGMP, while filled symbols are data measured with a cGMP concentration ramp. The mean value of the reversal potential measured at all cGMP concentrations in α channels (dashed line) is −5.2 mV. The continuous line is the modified Hill equation (Eq. 4) that best fits the data collected on αβ channels. The adjustable parameters are: K 1/2 = 45.4 μM, n = 2.45, min = −4.38 mV, and max = −8.0 mV. The same parameters define the Hill equation that best describes the dependence on cGMP of current amplitude measured at +15 mV in the same patch, under the same ionic conditions. (Bottom right) PCa/PNa as a function of [cGMP] measured in α (▴) and αβ (•) channels from the data on the left. The mean PCa/PNa for the α channel (dashed line) is 5.1. For the αβ channels, the same Hill function as on the left fits the data optimally with PCa/PNamin = 4.1 and PCa/PNamax = 8.8.