Figure 1.
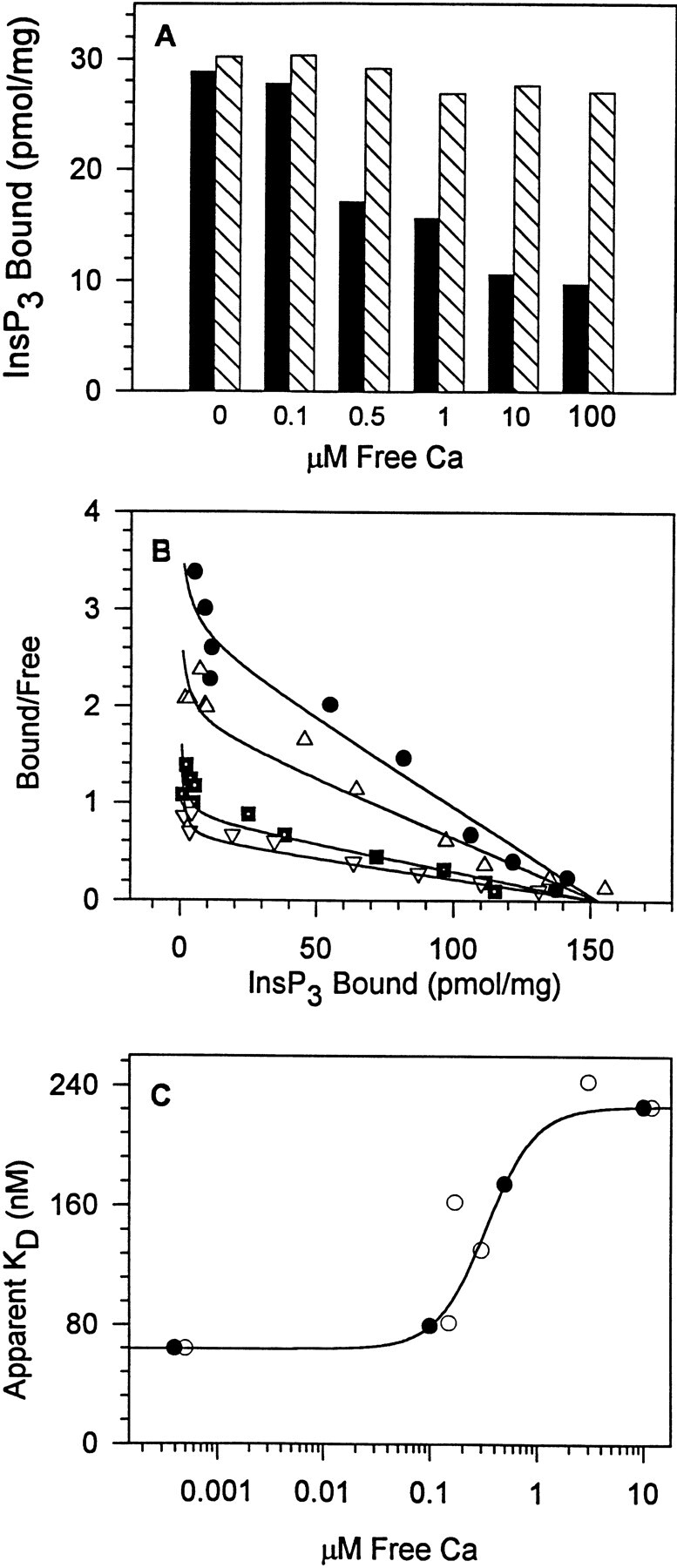
Micromolar Ca inhibits InsP3 binding to cerebellar membranes by increasing the K d for InsP3. (A) InsP3 binding decreased 66% when the Ca concentration was increased from 0 to 100 μM (solid bars), and this inhibition was fully reversible upon chelation of Ca by EGTA (hatched bars). The InsP3 concentration was 10 nM. One of three similar experiments. (B) Scatchard analysis indicated that Ca decreased InsP3 binding affinity without a change in maximal binding. Concentrations of Ca tested were 0.0004 (•), 0.1 (▵), 0.5 (▪), and 10 (▿) μM. Note that complete inhibition of InsP3 binding was not observed. (C) The K d values from B plotted as a function of the Ca concentration for two experiments (• and ○). The Ca-dependent increase in the K d for InsP3 binding increased 3.5-fold over the Ca concentration range tested with half maximal increase at 0.3 μM Ca (data were fit using a Hill equation with a coefficient n = 1.5).
