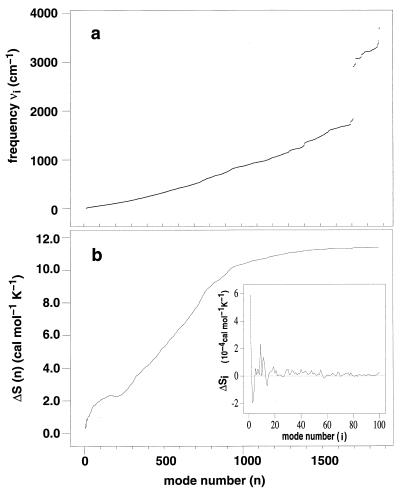
Figure 1.
(a) Vibrational spectra of unbound (P) and complexed (PW) bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (cannot be distinguished on this scale). The vibrational frequencies νi correspond to the normal modes of the energy-minimized structure (20) obtained by diagonalizing the mass-weighted matrix of the second derivatives of the energy (21). (b) Cumulative change of the vibrational entropy ΔS(n) = ∑i=1n ΔSi on water binding, where ΔSi = (SiPW − SiP) is the contribution of the ith vibration mode. The Inset shows ΔSi for the first 100 modes. Si = [hνi/T/(ehνi/kT − 1) − kln(1 − e−hνi/kT)] is the entropic content of one vibration mode i (12).