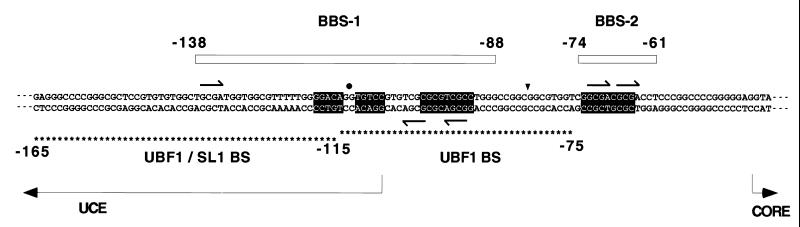
Figure 5.
Location of binding sites of basonuclin relative to those of UBF1. The sequence shown is that of the promoter region of the human rRNA gene (18). The upper strand is the RNA-like (coding) strand. The CORE region is essential for transcription but is not protected from nuclease digestion by either UBF1 or basonuclin. BBS1 and BBS2 are indicated by boxes. BBS1 contains a dyad sequence (black background), whose center is indicated by a black dot. BBS2 contains a dyad sequence whose complement is located near the 3′ end of BBS1. The axis of symmetry, indicated by a triangle, is located between nucleotides −82 and −83. The intervening 18-bp spacer consisting of 15 nucleotides is not protected from DNase I. The UBF1-binding region is shown by asterisks below the sequence. The 3′ half is protected by UBF1 alone (upper row of asterisks), and the 5′ half is protected only when SL1 is present as well (lower row of asterisks). BBS1 is centered almost at the same point as the entire binding region of UBF1. BBS2 is not protected by UBF1. Arrows indicate the repeated sequence GCGA, which occurs in both strands of the dyad sequence.