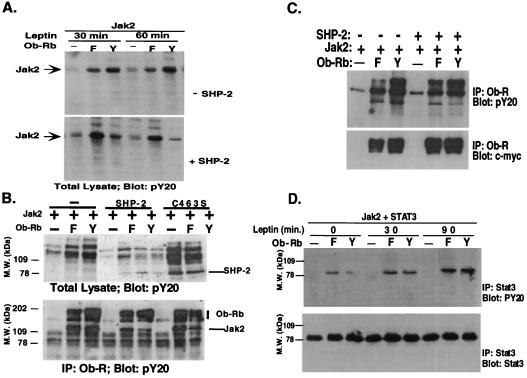
Figure 5.
Activation of SHP-2 leads to decreased phosphorylation of JAK2 but not Ob-Rb or STAT3. (A) SHP-2 decreases phosphorylation of JAK2. The level of phosphorylation of JAK2 was assayed after leptin treatment in cells transfected with the wild-type or Y→F 985 mutant. After leptin treatment, the level of JAK2 phosphorylation was severalfold greater in cells transfected with the wild-type receptor. When SHP-2 was cotransfected, the level of JAK2 phosphorylation was now greater in cells transfected with the Y→F 985 mutant. These data indicate that binding of leptin to Ob-Rb and activation of SHP-2 leads to a decrease in the level of phosphorylation of JAK2. (B) JAK2 dephosphorylation is a direct action of SHP-2. Cells were transfected as indicated and were treated with leptin. Total cellular lysate was blotted with pY20 (Upper), or Ob-Rb was first immunoprecipitated, followed by pY20 blotting (Lower). SHP-2 became hyperphosphorylated when C463S mutation was introduced. Tyrosyl phosphorylation of receptor-associated JAK2 was greatly reduced when wild-type receptor and SHP-2 were cotransfected, not when SHP-2 is replaced with SHP-2 C463S. (C) SHP-2 does not appreciably affect Ob-Rb tyrosyl phosphorylation. Ob-Rb Y→F (F) or wild-type (Y) receptor was transfected into 293T cells together with JAK2 with or without SHP-2. Cells were treated with leptin, and Ob-Rb was immunoprecipitated. PY20 and anti c-myc monoclonal antibodies were used to examine receptor tyrosyl phosphorylation and expression. (D) SHP-2 does not appreciably affect STAT3 tyrosyl phosphorylation. STAT3 was cotransfected into 293T cells together with the wild-type or Y→F receptor mutant. STAT3 phosphorylation was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and pY20 blotting. The amount of STAT3 protein was measured with a monoclonal antibody.