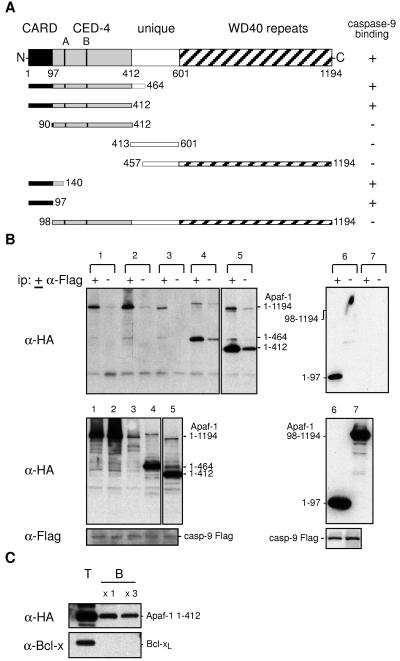
Figure 1.
Apaf-1 binds through its CARD to procaspase-9. (A) The wt and truncated human Apaf-1 proteins used in this study, all with a C-terminal HA tag, and their binding to procaspase-9. (B) The Apaf-1 CARD (residues 1–97) is necessary and sufficient for binding to procaspase-9. 293T cells were transiently cotransfected with a vector expressing mutant procaspase-9 Flag and ones expressing HA-tagged wt or mutant Apaf-1: wt (lane 1), Apaf-1 K149R (A box mutant) (lane 2), Apaf-1 KDD232/233AA (B box mutant) (lane 3), Apaf-1 (1–464) (lane 4), Apaf-1 (1–412) (lane 5), Apaf-1 (1–97) (lane 6), and Apaf-1 (98–1194) (lane 7). Lysates (1 mg protein) were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of monoclonal anti-FLAG M2, and the resulting immunoprecipitates were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and blotted with monoclonal anti-HA 3F10 antibody (Upper). Expression of procaspase-9 and Apaf-1 was confirmed by blots of lysates (Lower). The larger bands in lanes 4 and 5 represent aggregated Apaf-1 mutants. These data are representative of three experiments. Results with other Apaf-1 derivatives are summarized (A). (C) Apaf-1, particularly its N-terminal region, binds to Sepharose beads. Lysates (0.5 mg protein) from 293T cells transfected with vectors expressing Apaf-1 1–412 HA or Bcl-xL were mixed with 50% (vol/vol) Sepharose CL4B beads (Sigma) at 4°C for 1.5 h, and the beads then were washed once or three times with lysis buffer. Equivalent amounts of total (T) and Sepharose-bound (B) lysate then were Western-blotted. The data are representative of two experiments. Full-length Apaf-1 yielded lower background binding (see text).