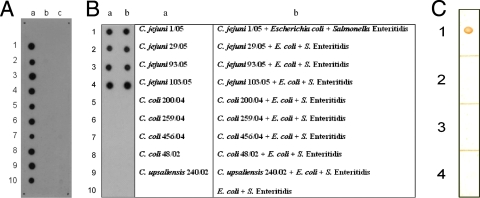
FIG. 1.
Dot blot analysis of the specificity of MAb5C4 for C. jejuni. (A) For pure cultures, approximately 105 bacterial cells were used on each spot and probed with MAb5C4. a1 to a10, C. jejuni isolates 1/05, 3/05, 5/05, 6/05, 8/05, 29/05, 78/05, 93/05, 103/05 and 104/05; b1 to b7, C. coli isolates 200/04, 202/03, 206/04, 207/04, 259/04, 416/04, and 456/04; b8 and b9, C. upsaliensis 240/02 and 239/02; b10, C. lari ATCC 35221; c1 to c5, E. coli isolates 130/05, 131/05, 132/05, 133/05, and 134/05; c6 to c10, Salmonella isolates 7/05, 17/05, 24/05, 30/05, and 47/05. (B) Comparison of MAb5C4 specificity in pure and mixed cultures. Approximately 105 bacterial cells were used on each spot and probed with MAb5C4. Suspensions of different bacteria were applied on the membrane according to the order of the table at right. The plus sign indicates that the spot is a mixture of bacterial cells from different genera. (C) Fecal sample of healthy chickens spiked with Campylobacter spp. and probed with MAb5C4. The dots represent fecal samples of healthy chickens spiked with approximately 105 CFU/ml of C. jejuni 103/05 (1), C. coli 200/04 (2), C. upsaliensis 240/02 (3), and C. lari ATCC 35221 (4).