FIG. 1. Reactive nitrogen species generation, DNA breakage, and PARP activation in diabetic blood vessels.
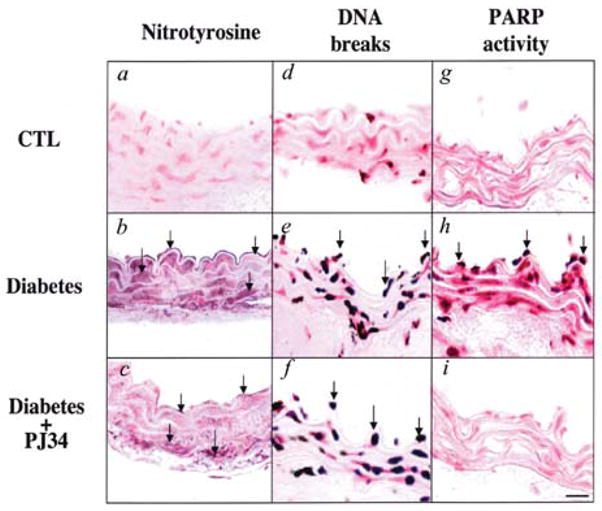
(a–c) Immunohistochemical staining for nitrotyrosine in control rings (a), in rings from diabetic mice treated with vehicle at 8 weeks (b), and in rings from diabetic mice treated with PJ34 (c). (d–f) Terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling, an indicator of DNA-strand breakage, in control rings (d), in rings from diabetic mice treated with vehicle at 8 weeks (e), and in rings from diabetic mice treated with PJ34 (f). (g–i) Immunohistochemical staining for poly(ADP-ribose), an indicator of PARP activation, in control rings (g), in rings from diabetic mice treated with vehicle at 8 weeks (h), and in rings from diabetic mice treated with PJ34 (i). Reproduced with permission from 33.
