Fig. 1.
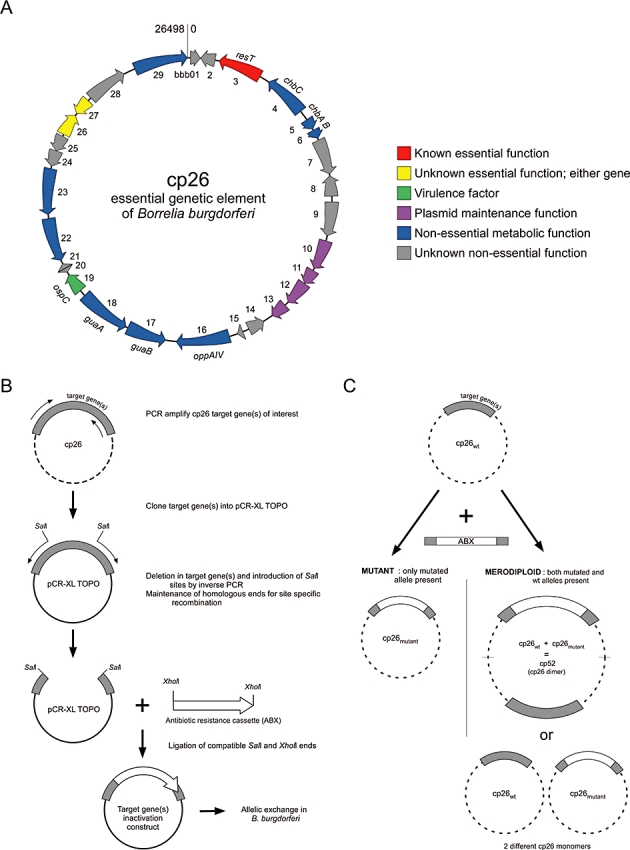
A. Graphical representation of cp26. The arbitrary position of bases 0/26498 is represented by a vertical line between bbb01 and bbb29 (Fraser et al., 1997). Genes are grouped according to functional class. Known essential function (red); unknown essential function (yellow); virulence factor (green); plasmid maintenance (purple); non-essential metabolic function (blue); unknown non-essential function (grey). B. Schematic diagram of the method used for targeted mutagenesis of most of the genes on cp26. Targeted mutagenesis was achieved by allelic exchange of an antibiotic resistance cassette with the gene(s) of interest. C. Graphical representation of the possible outcomes of allelic exchange with cp26 target genes. A single mutated copy of a gene(s) can be recovered if the gene(s) is non-essential for growth. Merodiploids are defined as clones that harbour both a wild-type and mutant copy of the target gene(s) within the same cell, in this case either on a single cp26 dimer (cp52) or on two separate, coexisting cp26 monomers.
