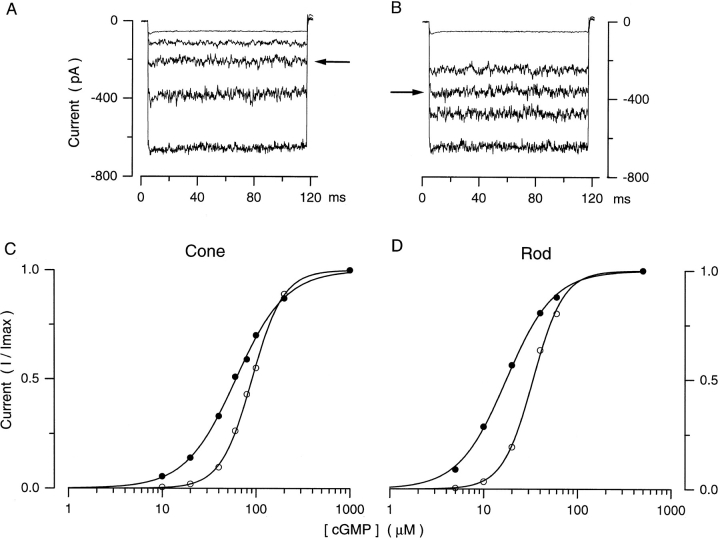
Figure 1.
Modulation of cGMP-dependent currents in detached membrane patches. A and B illustrate currents measured at room temperature in a patch detached from a cone outer segment. Currents were activated with voltage steps from 0 to −40 mV in the presence of 20 μM Ca++ and 100 μM Mg++ and various cGMP concentrations (shown are currents at 0, 40, 60 [arrow], 100 μM, and 1 mM). Currents shown in A were measured shortly after patch excision, while those in B were measured in the same membrane after exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution. The lower panels illustrate the dependence of normalized current amplitude on cGMP concentration at −40 mV before and after exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution. Data points were normalized by dividing the amplitude at each cGMP concentration tested (I) by the maximum current (Imax). C illustrates data measured in a patch detached from a cone outer segment. The continuous curve is the best fit to the data of the Hill equation (Eq. 1) with K 1/2 = 88.4 μM and n = 2.73 before exposure to EDTA/EGTA, and K 1/2 = 61.4 μM and n = 1.59 afterwards. D illustrates data measured in rod membrane patches, where the continuous curve is the Hill equation with K 1/2 = 34.2 μM and n = 2.3 before exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution, and K 1/2 = 17.9 μM and n = 1.6 afterwards.