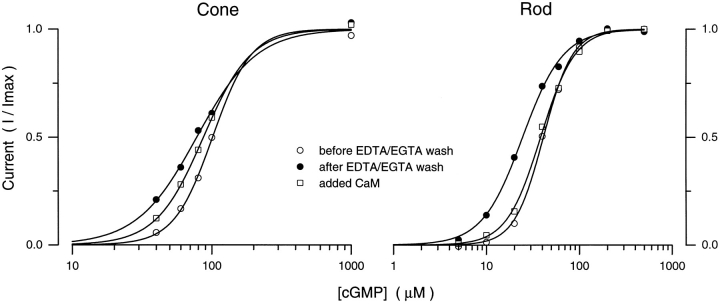
Figure 6.
Effect of calmodulin on modulation of cGMP-dependent currents in detached membrane patches. In cone or rod patches, currents were activated with voltage steps from 0 to −40 mV in the presence of 20 μM Ca++ and 100 μM Mg++ and varying concentrations of cGMP. Measurements were repeated in the same patch before and after exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution and in the continuous presence of 200 nM calmodulin. Data points were normalized by dividing current amplitude at each cGMP concentration (I) by the maximum current measured (Imax). The continuous line is the best fit to the data of the Hill equation (Eq. 1). In the cone patch, K 1/2 = 101 μM, n = 3.15 before exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution, K 1/2 = 78 μM, n = 2.0 afterwards, and K 1/2 = 87 μM, n = 2.55 in the presence of calmodulin. In the rod patch, K 1/2 = 41.2 μM, n = 2.78 before exposure to the EDTA/EGTA solution, K 1/2 = 24.6 μM, n = 1.98 afterwards, and K 1/2 = 39.4 μM, n = 2.47 in the presence of calmodulin.