Figure 4.
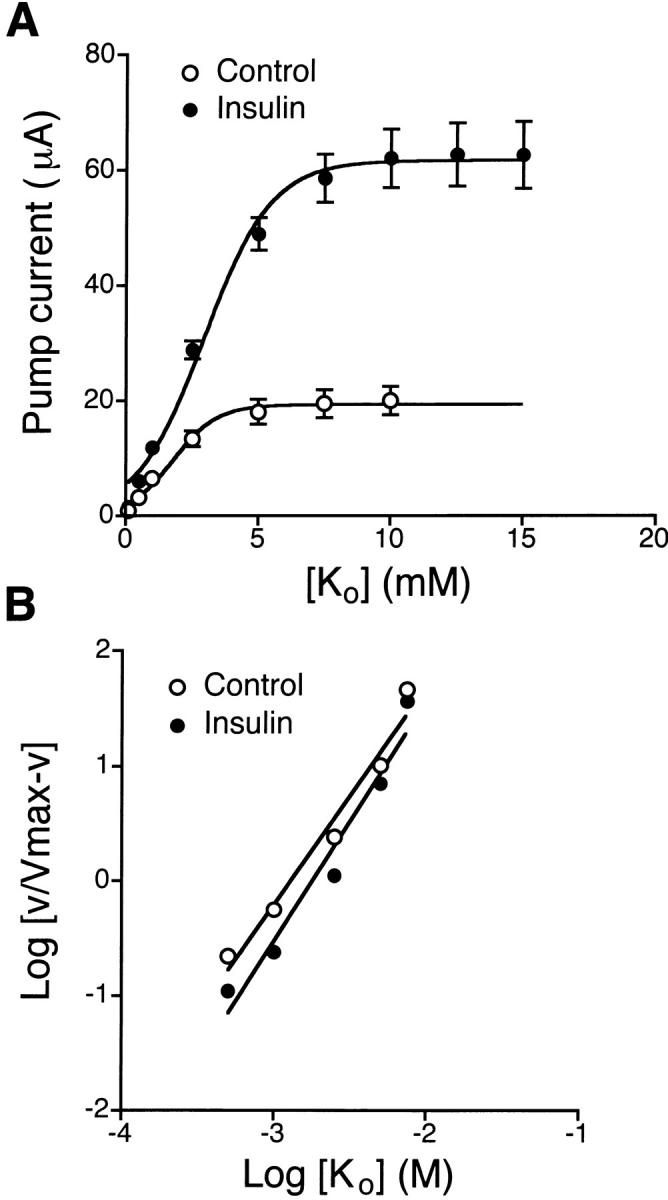
Extracellular [K+] dependence of pump current in control and insulin-treated monolayers. Experiments were performed using amphotericin B–permeabilized (apical membrane) monolayers bathed on both sides with NaMeSO4 Ringer solution. The cells were maintained in serum-free media (control) or serum-free media supplemented with 850 nM insulin for 4 d. (A) The pump current (I p) was plotted as a function of basolateral [K+]. The increase in [K+] in the basolateral solution was accomplished by replacement with KMeSO4 Ringer solution containing different concentrations of K+. Insulin treatment increased I max from 20 ± 2 μA (n = 11, N = 5) to 63 ± 6 μA (n = 9, N = 5) and increased K 0.5 from 1.8 ± 0.2 to 2.9 ± 0.2 mM (control, r 2 = 0.989; insulin, r 2 = 0.992). (B) Hill plot from the data shown in A. Insulin treatment did not significantly affect the Hill coefficient (control, 1.9 ± 0.2, r 2 = 0.971; insulin, 2.1 ± 0.3, r 2 = 0.956, estimated by linear regression analysis).
