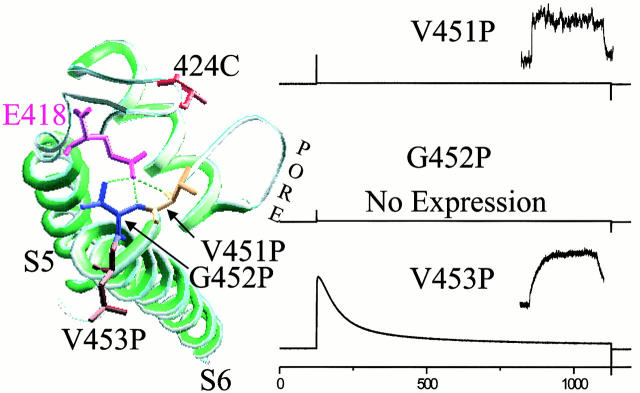
Figure 6.
Putative bonding partner for E418. Mutation of a residue predicted from the KcsA crystal structure to hydrogen bond with E418 has the same effect as mutation of E418. (Left) Top view of crystal structure of a single KcsA subunit. Shaker residues E418, its possible bonding partners V451 and G452, a control neighboring residue V453, and the fluorophore attachment site S424C are displayed with side chains at their homologous KcsA positions. Hydrogen bonds are possible between the E418 side chain and the backbone amino groups of either 451V and/or 452G, as defined by the Swiss Prot program. (Right) Ionic currents and fluorescence traces for 424C-TMRM (inset, right) are shown for proline substitutions. V451P is similar to the W434F, both in current (I) and fluorescence (F), which is consistent with a relative destabilization of the open conformation of the inactivation gate. Mutation of G452P prevented channel expression. V453P did not affect either the ionic current or the ΔF, indicating that there is no major structural perturbation because of proline substitution in this region.