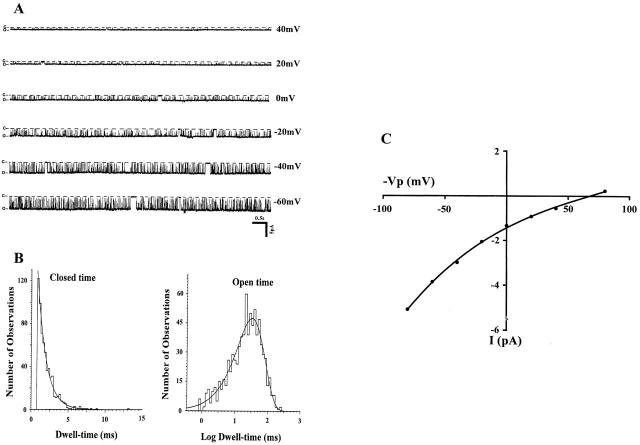
Figure 1.
A representative recording showing the kinetics of the apical small-conductance K channel in the mouse CCD. (A) Experiment was carried out in a cell-attached patch with pipette solution (mM): 140 KCl, 1.8 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES; and bath solution (mM): 140 NaCl, 5 KCl, 1.8 MgCl2, 1.8 CaCl2, and 10 HEPES. Different holding potentials (−Vp, from 40 to −60 mV) were applied and are indicated on right side of each trace. Channel closed and open states are indicated by C and O, respectively. (B) The channel open- and closed-time histograms. The mean closed time was 1.4 ± 0.01 ms and mean open time was 22.7 ± 0.03 ms. (C) I-V curve of the apical K channel. The slope conductance was 28.4 pS measured between −20 and 20 mV.