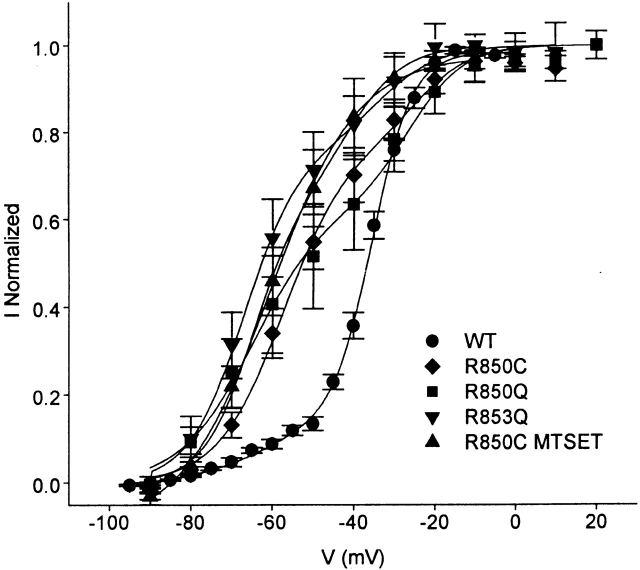
Figure 5.
Voltage dependence of Css IV-trapped sodium channels. Mean conductance-voltage relationships of Nav1.2, R850C/Q, R850C-MTSET, R853C/Q, and R853C-MTSEA in the presence of 200 nM Css IV after a +50 mV, 1 ms–prepulse. The solid lines through the data are fits to a sum of two Boltzmann relationships. The voltage dependence of the positive component was fixed to the half activation and slope values obtained from fits of the control channels to a single Boltzmann as shown in Table . The voltage for half activation (V1/2), slope factors (k), and the fraction of the total represented by the negative, toxin-shifted, component (Aneg) in these fits were the following: for Nav1.2a, V1/2 = −62.9 mV, k = 8.93 mV, Aneg = 0.13; for R850C, V1/2 = −57.4 mV, k = 7.9 mV, Aneg = 0.77; for R850C MTSET, V1/2 = −65.1 mV, k = 6.0 mV, Aneg = 0.64; for R850Q, V1/2 = −62.6 mV, k = 10.88 mV, Aneg = 0.70; and for R853Q, V1/2 = −67.0 mV, k = 6.80 mV, Aneg = 0.76.