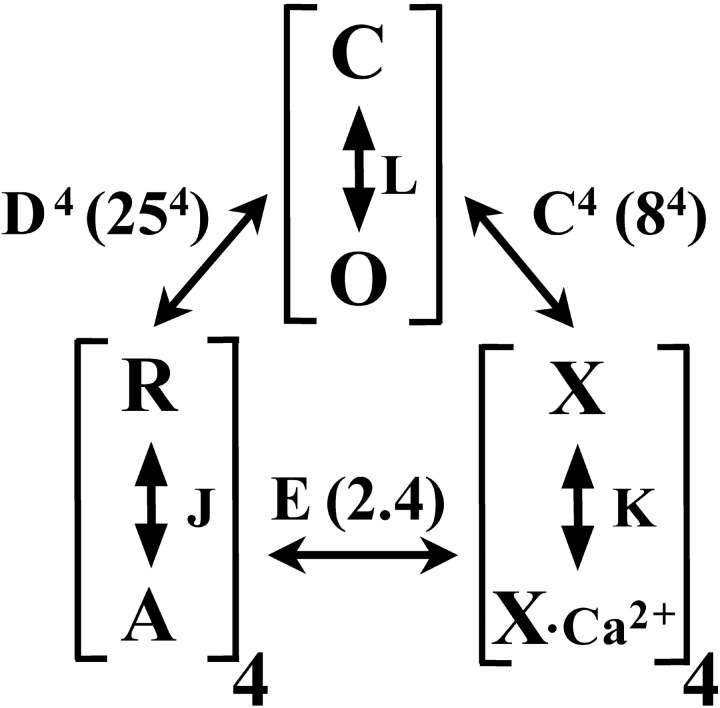
Figure 1.
Diagram of Scheme II (Horrigan and Aldrich, 2002) summarizing the allosteric relationships between channel opening, voltage-sensor movement, and Ca2+ binding in BK channel activation. Channel opening (C-O) is defined by equilibrium constant, L; voltage-sensor movement (R-A) is defined by equilibrium constant J, with 4 voltage-sensors per channel; Ca2+ binding (X-X*Ca2+) is defined by binding constant K with four binding sites per channel. The allosteric coupling factors are given by C–E, with values estimated by Horrigan and Aldrich given in parentheses. Although Ca2+ binding and voltage-sensor movement relatively independently regulate the C-O transition, voltage-sensor movement is ∼100-fold more effective. When there is no coupling between two processes, the allosteric coupling factor is 1.