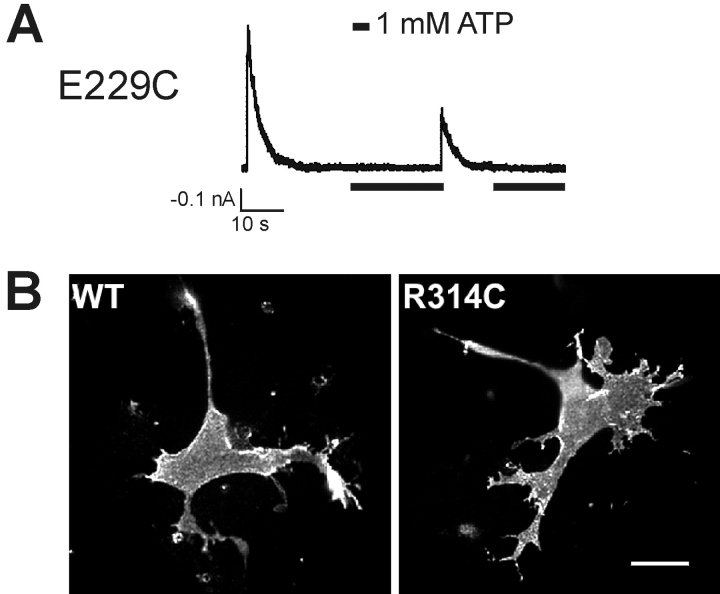
Figure 5.
Characterization of the E229C and the R314C mutant channels. (A) A representative current trace recorded from an inside-out membrane patch containing the E229C mutant channels. The channels displayed inactivation similar to that observed in the E229A and E229R channels upon patch excision into the K-INT/EDTA solution. Exposure to 1 mM ATP (indicated by black bars below the recordings) partially reactivated the channels, which again underwent rapid inactivation. (B) The R314C Kir6.2 mutant protein is expressed and incorporated into the KATP channel complex. Surface immunofluorescent staining of cells coexpressing FLAG-tagged SUR1 and either the WT or the R314C mutant Kir6.2. Immunostaining was performed in living cells at 4°C using the M2 anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody followed by Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody. Surface labeling of the FLAG-SUR1 was observed in both cells coexpressing the WT or the R314C mutant Kir6.2, demonstrating that the R314C Kir6.2 is properly incorporated into the KATP channel complex.