TABLE I.
Intraburst Open and Closed States
| Intraburst open states | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vm |
|
τo(b)1 |
|
τo(b)2 |
|
τo(b)3 | n T | |||||
| mV | ||||||||||||
| −50 | 0.552 | 0.15 | 0.439 | 0.391 | 0.009 | 2.607 | 1,993 | |||||
| −40 | 0.349 | 0.301 | 0.637 | 0.816 | 0.014 | 2.957 | 7,892 | |||||
| −30 | 0.482 | 0.611 | 0.5 | 1.839 | 0.019 | 4.622 | 5,849 | |||||
| −20 | 0.613 | 0.837 | 0.339 | 3.093 | 0.048 | 8.281 | 2,984 | |||||
| −10 | 0.407 | 0.646 | 0.494 | 3.11 | 0.1 | 13.864 | 3,337 | |||||
| 0 | 0.312 | 1.819 | 0.597 | 8.136 | 0.09 | 23.328 | 554 | |||||
| Intraburst closed states | ||||||||||||
| Vm |
|
τo(b)1 |
|
τo(b)2 | n T | |||||||
| mV | ||||||||||||
| −50 | 0.517 | 0.63 | 0.483 | 1.585 | 2,093 | |||||||
| −40 | 0.935 | 0.348 | 0.065 | 1.278 | 5,586 | |||||||
| −30 | 0.956 | 0.324 | 0.044 | 1.746 | 3,047 | |||||||
| −20 | 0.853 | 0.228 | 0.147 | 0.899 | 1,145 | |||||||
| −10 | 0.819 | 0.37 | 0.181 | 1.543 | 1,334 | |||||||
| 0 | 0.783 | 0.314 | 0.217 | 1.5 | 169 | |||||||
Kinetic parameters obtained from the analysis of frequency distribution diagrams of intraburst open times (top) and intraburst closed times (bottom) of persistent Na+ channel openings. Data were from 10 different patches. Open-time and closed-time histograms were fitted with triple or double exponential functions, respectively (see materials
and
methods, Eq. 1). The fitting parameters thus obtained at various test potentials (V
m), namely time constants (τs) and relative weight coefficients (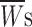 ), are specified. Relative weight coefficients were calculated as:
), are specified. Relative weight coefficients were calculated as: 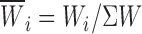 . n
T is the total number of observations in each histogram.
. n
T is the total number of observations in each histogram.