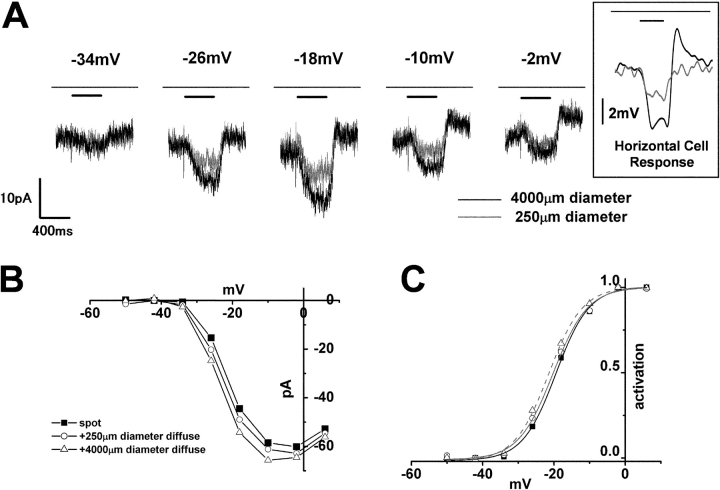
Figure 6.
Effects of the diameter of illumination on the surround response of a cone photoreceptor. (A) Surround response of a cone photoreceptor to small (diameter, 250 μm; gray trace) and large (diameter, 4,000 μm; black trace) surround illumination recorded at various holding voltages (indicated on each trace). Diffuse light (duration, 400 ms) illumination was given during the step depolarization (shorter bar) in the presence of small spot light (diameter, 30 μm; top bar). (Boxed inset) Voltage response of a HC to small (diameter, 250 μm; gray trace) and large (diameter, 4,000 μm; black trace) surround illumination. The voltage trace was low-pass filtered at 20 Hz. Diffuse light illumination was given during the step depolarization (shorter bar) in the presence of small spot light (top bar). (B) I-V curve of the ICa of the cone shown in A. Filled squares, without surround illumination; open circles, during small (diameter, 250 μm) surround illumination; open triangles, during large (diameter, 4,000 μm) surround illumination. The current was measured at its peak. (C) Activation curves fitted to the Boltzmann function derived from the data in B, showing a lateral shift of the mid point from −17.4 mV (no surround illumination, black solid line) to −20.3 mV (small surround illumination, thin line), and −21.5 mV (large surround illumination, broken line). The maximum conductance was determined from the linear part of the data curve, between −2 and 6 mV, obtained following diffuse light illumination in the control solution, and was normalized to 1.0.