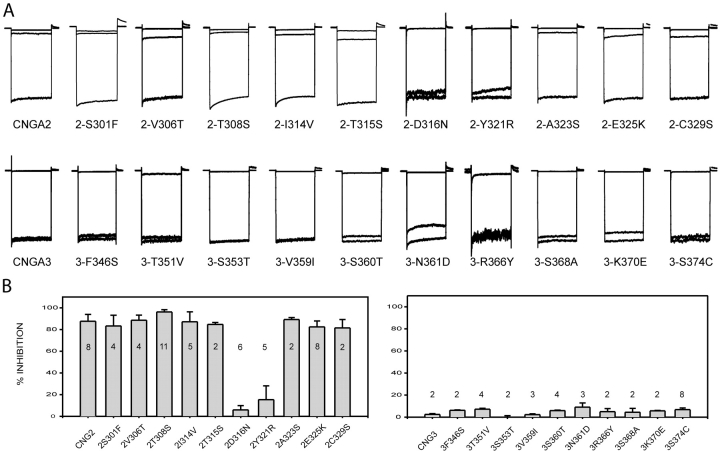
Figure 4.
Identification of amino acid residues involved in PsTx binding. Point mutations were made to exchange amino acids differences between CNGA2 and CNGA3. All current was normalized to facilitate comparison. (A) Currents were measured at −60 mV in control (bottom trace), 10 mM MgCl2 (top trace), and 500 nM PsTx (middle trace) for each mutant channel. PsTx blocked all CNGA2 mutants, except 2-D316N and 2-Y321R, with high affinity. Inhibition of 2-D316N and 2-Y321R by 500 nM PsTx was reduced to <5%. No single point mutation was sufficient to confer high affinity PsTx block upon CNGA3. A significant improvement in the block was only observed in the 3-N366Y channel (15 ± 3%). (B) Histogram comparing block of all mutant channels by 500 nM PsTx. Maximum patch currents were >1 nA for all mutant channels, except for 2-D316N and 2-Y321R, which were between 0.5 and 0.8 nA, and 3-R366Y and 3-S374C, which were between 0.1 and 0.3 nA. Error bars indicate standard deviation, and n values are shown.