Figure 1.
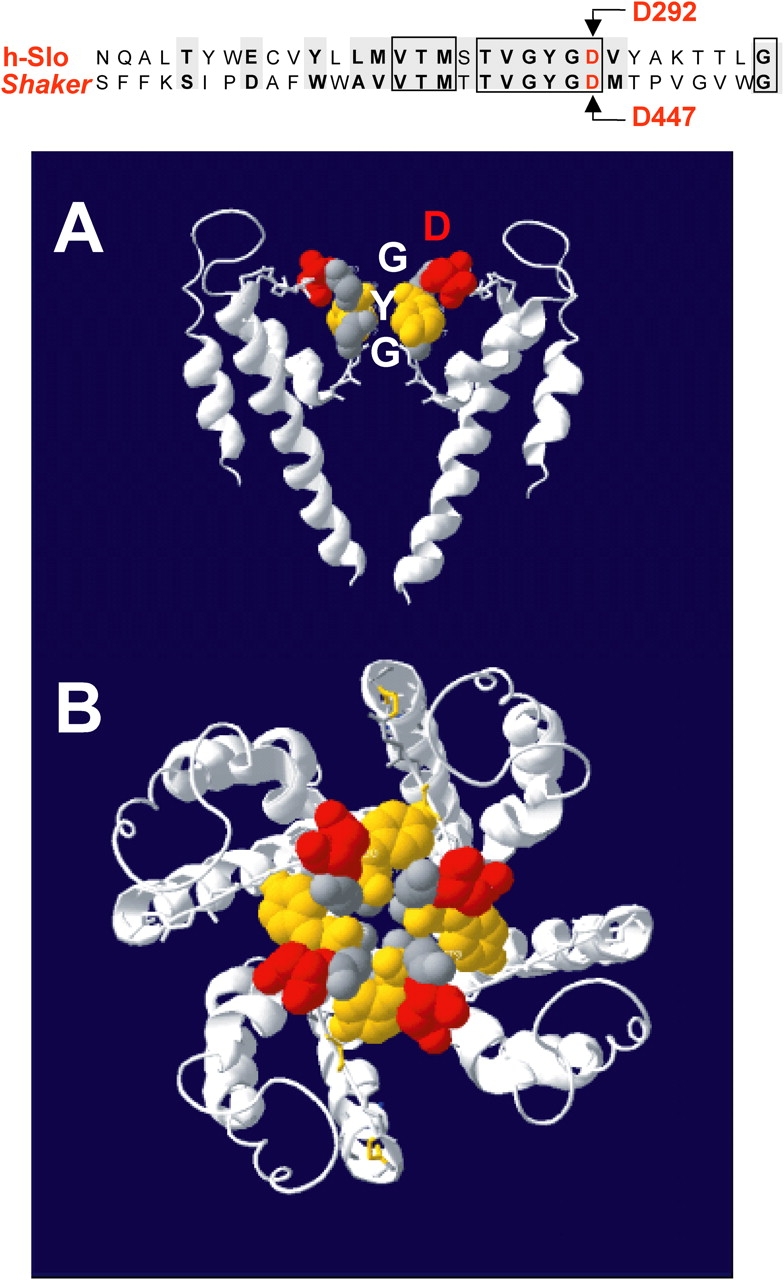
The D292N mutation neutralizes the negatively charged aspartic acid in the GYGD selectivity filter of the pore. The top panel shows the amino acid sequence alignment corresponding to the pore regions of hSlo and Shaker K+ channels. The boxes enclose identical amino acids, while gray background shows residues with conserved properties. (A) Two of the four monomers that constitute a functional K+ channel based on the crystal structure of KcsA proposed by Doyle et al. (1998). A probable arrangement of the conserved sequence of the pore region corresponding to the selectivity filter is shown. (B) The arrangement of all four monomers viewed from the top, revealing the central pore of the conduction pathway and the position of the four aspartates (red) lining the pore vestibule.
