Fig. 6.
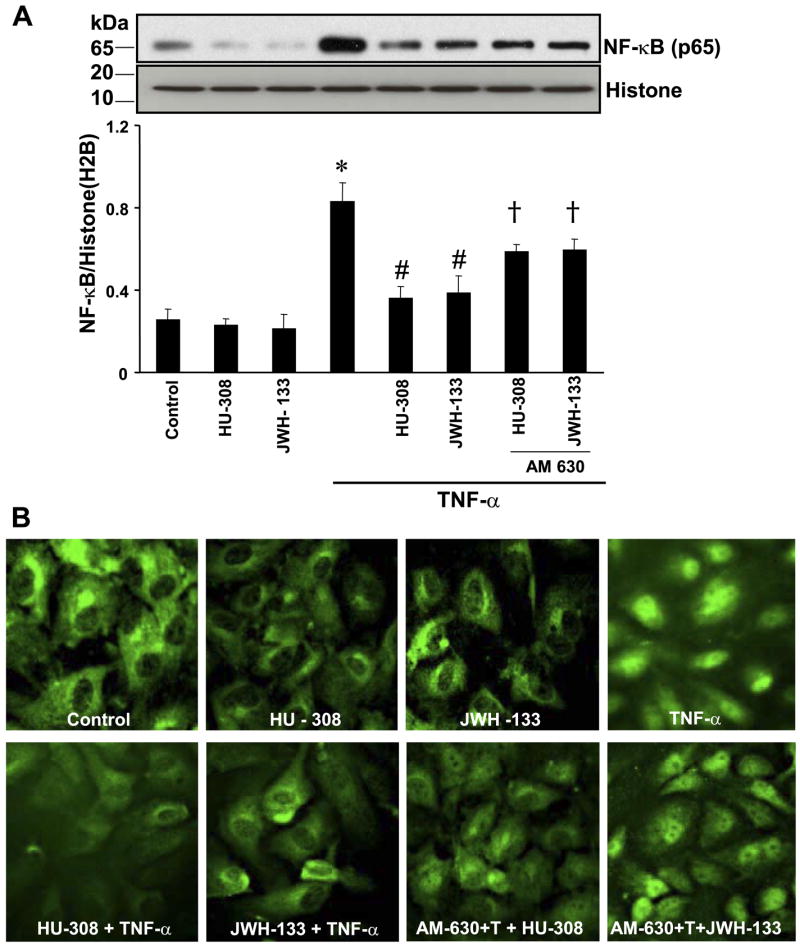
CB2 agonists decrease TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in HCAECs. A: cells were treated with TNF-α ± HU-308 or JWH-133 (3 μM) for 6 h or pretreated with CB2 antagonists (1 μM) followed by treatment with TNF-α ± HU-308 or JWH-133 for 6 h. Nuclear extracts were then prepared, and NF-κB expression was determined by Western immunoblot assay; n = 3 samples. *P < 0.05 vs. control; #P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α; †P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α + HU-308 or JWH-133. B: activation of NF-κB by TNF-α in HCAECs, and CB2 agonists inhibit NF-κB activation. Note the intense nuclear staining of NF-κB (p65) in cells exposed to TNF-α and the faint staining indicating that CB2 agonists diminished TNF-α activation of NF-κB. Shown are representative images from 3 separate experiments.
