Fig. 2. In vivo/in vitro target specificity assay.
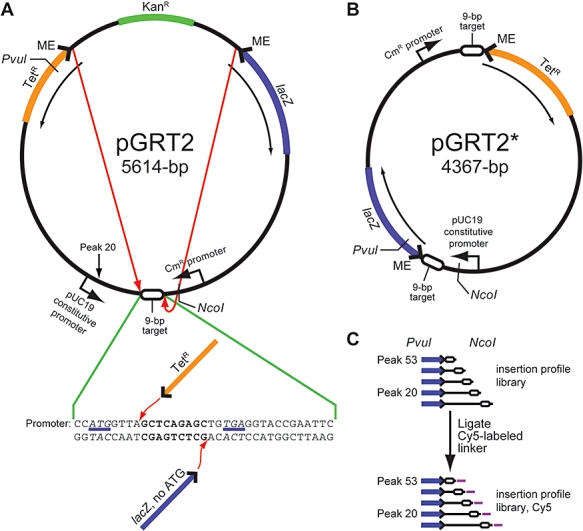
A. This assay utilizes the rescue of a TetR gene to measure transposition frequency and the rescue of a LacZ gene (that is missing a start codon) to measure specific insertion events into a designed, preferable 9 bp target site (GCTCAGAGC). Insertions into this 9 bp target site corresponds to peak 53 in Fig. 3. A second preferable target site is native to plasmid pGRT2 and is noted as peak 20 (see Fig. 3). These experiments were repeated twice at multiple dilutions for each mutant Tnp.
B. One possible insertion event out of the library of insertion events is shown. This plasmid represents specific insertion into the 9 bp target site and corresponds to peak 53 in Fig. 3.
C. This is a schematic representing the analysis of insertion fragments. After transposition, the library is digested with NcoI and PvuI to generate insertion fragments. The PvuI site is located within the transposon and represents a fixed position. The NcoI site is located within the target DNA. Fragment length is determined by an insertion event relative to the NcoI site and allows us to analyse fragments that contain insertion events that begin near the specific 9 bp target site and extend out to ∼300 bp from the specific target site. After digestion, these fragments were labelled via the ligation of small, 5′-Cy5-labelled DNA to the insertion fragments that allow for visualization of the fragments through PAGE.
