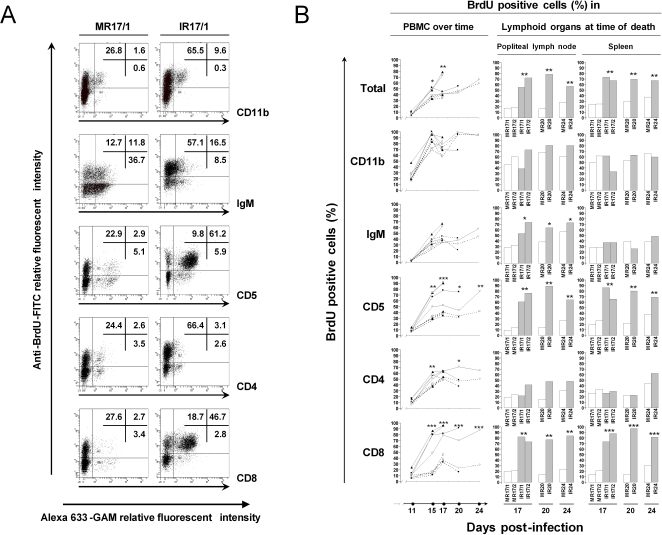
Figure 2. Analysis of in vivo BrdU incorporation.
Rabbits were treated as described in Fig. 1. PBMCs were collected at days 11, 15, 17, 20 and 24 post-inoculation, while mononuclear cells were isolated from popliteal lymph node and spleen at the time of death. Cells were labelled with anti-CD11b, IgM, CD5, CD4 and CD8 mAbs as the primary antibodies. Alexa 633-GAM was used as the secondary antibody. In vivo BrdU incorporation was revealed by immunofluorescent staining as described in Methods. After staining, cells were analysed by flow cytometry. A. Representative flow cytometry dot plots are shown for each double staining, they illustrate the data obtained at day 17 post-infection for the PBMC of rabbits MR17/1 and IR17/1. The data represent the percentages of BrdU positive cells (y-axis) calculated based on the acquisition of 10,000 cells expressing the indicated cell marker (x-axis). B. The percentage of BrdU positive cells amongst the indicated cellular subset was determined and compared between AlHV-1 infected (left column: bold lines; middle and right columns: hatched bars) and mock infected (left column: dotted lines; middle and right columns: open bars) groups (* P<0.05; **P<0.005, *** P<0.0001). In the left column the following symbols were used: ▴, MR17/1 and IR17/1; □, MR17/2 and IR17/2; •, MR20 and IR20; ○, MR24 and IR24.