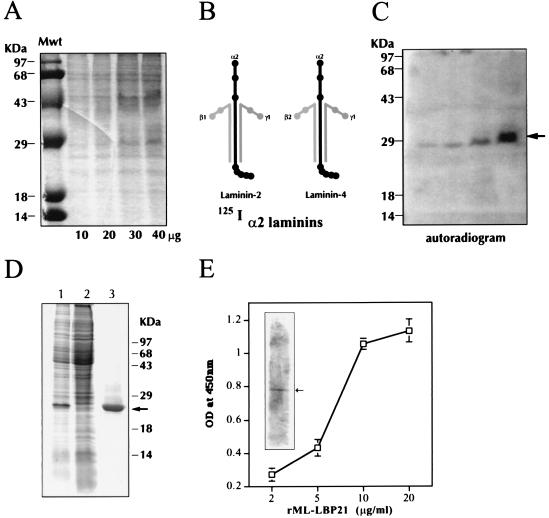
Figure 1.
Identification, expression, and characterization of ML-LBP21. (A–C) Identification of α2-laminin-binding protein from M. leprae cell wall fraction. (A) Increasing concentration of M. leprae cell wall fraction (10–40 μg/ml per lane) was separated by SDS/10% PAGE and stained with Coommassie brilliant blue. Molecular mass markers (Mwt) are indicated on the extreme left lane. (B) Diagram of human α2-laminins (a mixure of laminin-2 and laminin-4) and their chain specificity are shown. (C) Identical gels containing M. leprae cell wall fraction (10–40 μg/ml) was transferred to PVDF membrane and probed with 125I-labeled α2-laminins, and bound laminin was detected by autoradiography. The arrow indicates the binding of α2-laminins to a 28-kDa band in the cell wall fraction in a concentration-dependent manner. (D) Expression and purification of recombinant ML-LBP21. ML-LBP21 was expressed as His-tagged fusion protein, purified on a Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid resin, and separated by SDS/PAGE. The gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Lane 1, lysates of isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG)-induced culture; lane 2, uninduced culture; lane 3, affinity-purified recombinant protein. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are shown on the right, and the arrow indicates the purified rML-LBP21. (E) Characterization of rML-LBP21 binding to α2-laminins. The binding of biotinylated α2-laminins to rML-LBP21 as detected by ELISA and immunoblotting (Inset) by using streptavidin method. The arrow in the inset indicates the rML-LBP21-bound α2-laminins.