Abstract
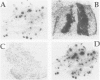
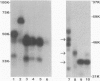
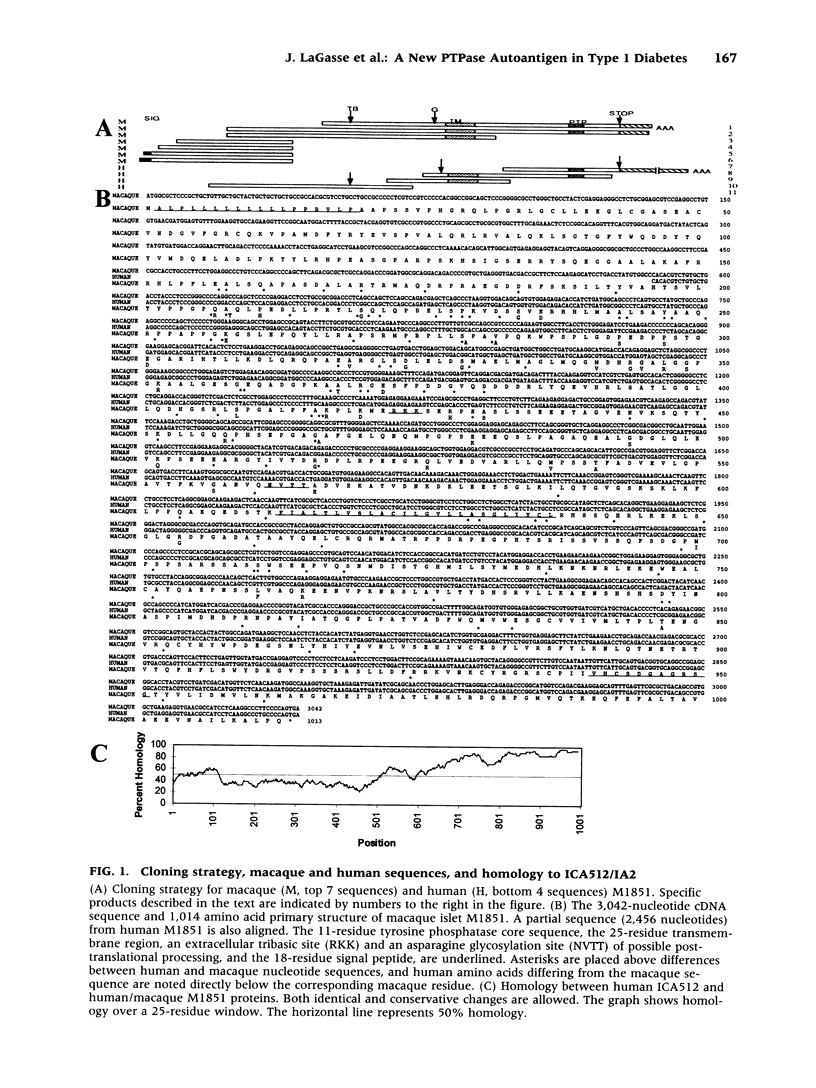
BACKGROUND: We sought to identify novel islet-cell autoantigens to better understand the pathogenesis, prediction, and immunotherapy of type 1 diabetes. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Macaque and human islet cDNA libraries expressed in mammalian cells were screened with human diabetes sera. A positive clone was sequenced directly and after 5' rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE). Northern blotting and in situ hybridization revealed the tissue distribution of the corresponding protein. Antigen, expressed by in vitro translation, and tryptic peptides were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. For the immunoprecipitations, 183 diabetic, 60 prediabetic, and 91 control sera were used. Truncated antigens were used in immunoprecipitations for epitope mapping. Recombinant antigen expressed in transfected fibroblasts was used in competition assays. RESULTS: Sequencing yielded an 111-kDa, 1,013 amino acid, transmembrane protein (M1851) containing consensus protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) sequence. M1851 was 77% identical in the intracellular domain, but only 31% identical extracellularly, to the islet-cell autoantigen ICA512. mRNA localized to brain, prostate, pancreatic islets, and adrenal medulla. After limited trypsinization, the in vitro translated antigen was 37 kDa. M1851 was recognized by 47% of prediabetes sera, 31% of new diabetes sera, but only 1% of healthy controls. Only 1/73 sera binding M1851 failed to bind ICA512, whereas 42/114 binding ICA512 did not bind M1851. M1851 reactivity was not fully displaced by ICA512 in 24/49 sera. Removing the C-terminal 27, 80, or 160 amino acids of M1851 decreased reactivity by 70%, 90%, and 100%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: This new islet-cell PTPase is likely to be the precursor to the 37-kDa tryptic fragment antigen. It is structurally related to ICA512 but has distinct diabetes autoantibody epitopes located at the C terminus.
Full text
PDF




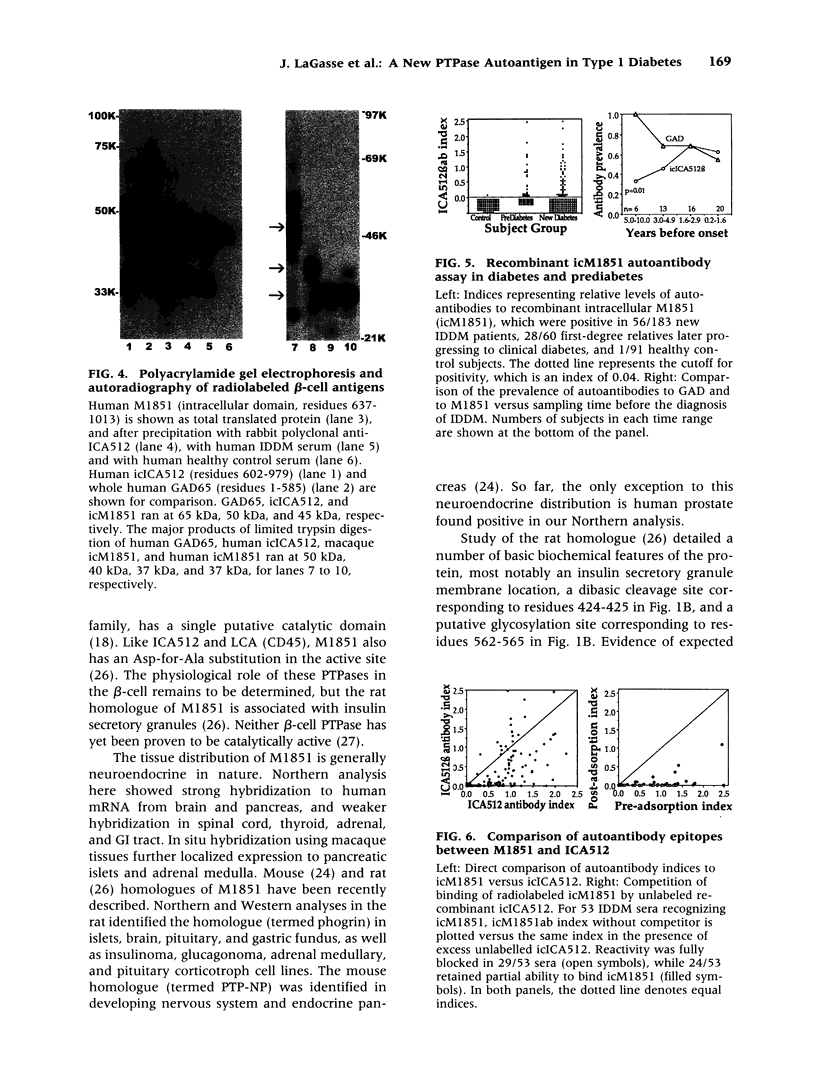




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aanstoot H. J., Kang S. M., Kim J., Lindsay L. A., Roll U., Knip M., Atkinson M., Mose-Larsen P., Fey S., Ludvigsson J. Identification and characterization of glima 38, a glycosylated islet cell membrane antigen, which together with GAD65 and IA2 marks the early phases of autoimmune response in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 15;97(12):2772–2783. doi: 10.1172/JCI118732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Diosdado M., Parkinson D., Corbett J. A., Kwon G., Marshall C. A., Gingerich R. L., Santiago J. V., McDaniel M. L. Potential autoantigens in IDDM. Expression of carboxypeptidase-H and insulin but not glutamate decarboxylase on the beta-cell surface. Diabetes. 1994 Mar;43(3):418–425. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arden S. D., Roep B. O., Neophytou P. I., Usac E. F., Duinkerken G., de Vries R. R., Hutton J. C. Imogen 38: a novel 38-kD islet mitochondrial autoantigen recognized by T cells from a newly diagnosed type 1 diabetic patient. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 15;97(2):551–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI118448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Bowman M. A., Kao K. J., Campbell L., Dush P. J., Shah S. C., Simell O., Maclaren N. K. Lack of immune responsiveness to bovine serum albumin in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1853–1858. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Holmes L. A., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Maclaren N. K. No evidence for serological autoimmunity to islet cell heat shock proteins in insulin dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):721–724. doi: 10.1172/JCI115051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Kaufman D. L., Campbell L., Gibbs K. A., Shah S. C., Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J., Maclaren N. K. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):458–459. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K. The pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 24;331(21):1428–1436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411243312107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Marner B., Bilde T., Ludvigsson J., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):167–169. doi: 10.1038/298167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingley P. J., Christie M. R., Bonifacio E., Bonfanti R., Shattock M., Fonte M. T., Bottazzo G. F., Gale E. A. Combined analysis of autoantibodies improves prediction of IDDM in islet cell antibody-positive relatives. Diabetes. 1994 Nov;43(11):1304–1310. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.11.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk E., Berne C., Kämpe O., Wibell L., Oskarsson P., Karlsson F. A. Diazoxide treatment at onset preserves residual insulin secretion in adults with autoimmune diabetes. Diabetes. 1996 Oct;45(10):1427–1430. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.10.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Genovese S., Braghi S., Bazzigaluppi E., Lampasona V., Bingley P. J., Rogge L., Pastore M. R., Bognetti E., Bottazzo G. F. Islet autoantibody markers in IDDM: risk assessment strategies yielding high sensitivity. Diabetologia. 1995 Jul;38(7):816–822. doi: 10.1007/s001250050358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Lampasona V., Genovese S., Ferrari M., Bosi E. Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatase-like IA2 (islet cell antigen 512) as the insulin-dependent diabetes-related 37/40K autoantigen and a target of islet-cell antibodies. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 1;155(11):5419–5426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1279–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady-Kalnay S. M., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as adhesion receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):650–657. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Josefsen K., Rygaard J., Spitalnik S. L. Pancreatic islet-cell epitope recognized by an anti-sulphatide monoclonal antibody. APMIS. 1991 Dec;99(12):1151–1156. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb01312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang M. K., Flanagan J. G. PTP-NP, a new member of the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase family, implicated in development of nervous system and pancreatic endocrine cells. Development. 1996 Jul;122(7):2239–2250. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.7.2239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christgau S., Aanstoot H. J., Schierbeck H., Begley K., Tullin S., Hejnaes K., Baekkeskov S. Membrane anchoring of the autoantigen GAD65 to microvesicles in pancreatic beta-cells by palmitoylation in the NH2-terminal domain. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):309–320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. R., Hollands J. A., Brown T. J., Michelsen B. K., Delovitch T. L. Detection of pancreatic islet 64,000 M(r) autoantigens in insulin-dependent diabetes distinct from glutamate decarboxylase. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):240–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI116556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. R., Vohra G., Champagne P., Daneman D., Delovitch T. L. Distinct antibody specificities to a 64-kD islet cell antigen in type 1 diabetes as revealed by trypsin treatment. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):789–794. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. E. Structure and catalytic properties of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 7;766:18–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb26644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathman C. G. Peptides as therapy of autoimmune disease. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1993 Dec;9(4):239–244. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian W. A., Karlsen A. E., Gottsäter A., Landin-Olsson M., Grubin C. E., Sundkvist G., Petersen J. S., Boel E., Dyrberg T., Lernmark A. Quantitative assay using recombinant human islet glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) shows that 64K autoantibody positivity at onset predicts diabetes type. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):368–374. doi: 10.1172/JCI116195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian W. A., Karlsen A. E., Petersen J. S., Teague J., Gervassi A., Jiang J., Fujimoto W., Lernmark A. Regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase diabetes autoantigen expression in highly purified isolated islets from Macaca nemestrina. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2674–2681. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian W. A., Sanjeevi C. B., Kockum I., Landin-Olsson M., Karlsen A. E., Sundkvist G., Dahlquist G., Palmer J., Lernmark A. Glutamate decarboxylase-, insulin-, and islet cell-antibodies and HLA typing to detect diabetes in a general population-based study of Swedish children. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1505–1511. doi: 10.1172/JCI117822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. I., Robbins D. C. Prevalence of adult-onset IDDM in the U.S. population. Diabetes Care. 1994 Nov;17(11):1337–1340. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.11.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Crosbie J., Brink R., Kantor A. B., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination from peripheral lymphoid tissues of self-reactive B lymphocytes recognizing membrane-bound antigens. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):765–769. doi: 10.1038/353765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Durinovic-Bello I., Ziegler A. G. Relation between cellular and humoral immunity to islet cell antigens in type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun. 1996 Jun;9(3):427–430. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1996.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek L. J., Lok S., Rosenberg G. B., Smith R. A., Grant F. J., Biggs S., Bensch P. A., Kuijper J. L., Sheppard P. O., Sprecher C. A. Expression cloning and signaling properties of the rat glucagon receptor. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1614–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.8384375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Grubin C. E., Dube S., Disteche C. M., Adler D. A., Bärmeier H., Mathewes S., Grant F. J., Foster D. Cloning and primary structure of a human islet isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase from chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8337–8341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Nakanishi K., Murase T., Kosaka K. Small doses of subcutaneous insulin as a strategy for preventing slowly progressive beta-cell failure in islet cell antibody-positive patients with clinical features of NIDDM. Diabetes. 1996 May;45(5):622–626. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.5.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. Immune intervention in type I diabetes mellitus--current clinical and experimental approaches. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1994;102(4):269–272. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori M., Kikuchi O., Sakuma T., Funaki J., Kitada M., Kamataki T. Molecular cloning of monkey liver cytochrome P-450 cDNAs: similarity of the primary sequences to human cytochromes P-450. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 29;1171(2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90113-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampasona V., Bearzatto M., Genovese S., Bosi E., Ferrari M., Bonifacio E. Autoantibodies in insulin-dependent diabetes recognize distinct cytoplasmic domains of the protein tyrosine phosphatase-like IA-2 autoantigen. J Immunol. 1996 Sep 15;157(6):2707–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan M. S., Lu J., Goto Y., Notkins A. L. Molecular cloning and identification of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2, from human insulinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 May;13(5):505–514. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Li Q., Xie H., Chen Z. J., Borovitskaya A. E., Maclaren N. K., Notkins A. L., Lan M. S. Identification of a second transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2beta, as an autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: precursor of the 37-kDa tryptic fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 19;93(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Notkins A. L., Lan M. S. Isolation, sequence and expression of a novel mouse brain cDNA, mIA-2, and its relatedness to members of the protein tyrosine phosphatase family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 28;204(2):930–936. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. O., Høyer P. E., Petersen J. S., Hejnaes K. R., Genovese S., Dyrberg T., Bottazzo G. F. Contribution of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies to the reactivity of islet cell cytoplasmic antibodies. J Autoimmun. 1994 Aug;7(4):497–508. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1994.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag B., Mukku P. V., Arimilli S., Phan D., Deshpande S. V., Winkelhake J. L. Antigenic peptide binding to MHC class II molecules at increased peptide concentrations. Mol Immunol. 1994 Oct;31(15):1161–1168. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ongagna J. C., Levy-Marchal C. Anti-37kDa antibodies are associated with the development of IDDM in individuals with islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia. 1995 Mar;38(3):370–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00400644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payton M. A., Hawkes C. J., Christie M. R. Relationship of the 37,000- and 40,000-M(r) tryptic fragments of islet antigens in insulin-dependent diabetes to the protein tyrosine phosphatase-like molecule IA-2 (ICA512). J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1506–1511. doi: 10.1172/JCI118188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin D. U., Pleasic S. M., Palmer-Crocker R., Shapiro J. A. Cloning and expression of IDDM-specific human autoantigens. Diabetes. 1992 Feb;41(2):183–186. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin D. U., Pleasic S. M., Shapiro J. A., Yoo-Warren H., Oles J., Hicks J. M., Goldstein D. E., Rae P. M. Islet cell antigen 512 is a diabetes-specific islet autoantigen related to protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):3183–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O. T-cell responses to autoantigens in IDDM. The search for the Holy Grail. Diabetes. 1996 Sep;45(9):1147–1156. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.9.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada A., Charlton B., Taylor-Edwards C., Fathman C. G. Beta-cell destruction may be a late consequence of the autoimmune process in nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1996 Aug;45(8):1063–1067. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.8.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. M., Ginsberg-Fellner F., McEvoy R. C. Strong association between diabetes and displacement of mouse anti-rat insulinoma cell monoclonal antibody by human serum in vitro. Diabetes. 1990 Oct;39(10):1203–1211. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.10.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verge C. F., Gianani R., Kawasaki E., Yu L., Pietropaolo M., Jackson R. A., Chase H. P., Eisenbarth G. S. Prediction of type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1996 Jul;45(7):926–933. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.7.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]