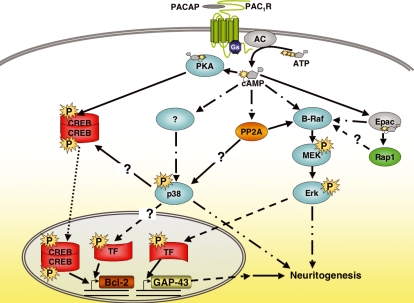
Fig. 8.
Proposed model for the cAMP-dependent signaling events involved in the neurotrophic actions of PACAP-38 on SH-SY5Y cells. PACAP-38 binding to the PAC1 receptor, which couples to the activation of AC, evokes an increase in the intracellular levels of cAMP (Lutz et al. 2006). This in turn leads to the activation of PKA-dependent and PKA-independent mechanisms that are involved in the induction of expression of neuronal proteins and in neuritogenesis, respectively. The PKA-dependent mechanism involves PKA phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB, initiating its activation and translocation to the nucleus where it may be involved in the up-regulated expression of proteins involved in neuronal differentiation, including Bcl-2. The PKA-independent mechanisms involve activation of MEK and ERK as well as p38 MAP kinase that are required for neuritogenesis. The MEK/ERK activation possibly occurs through one or a combination of different mechanisms. The neuronal MAP kinase signaling cascade involves B-Raf as the first component (Dugan et al. 1999) and it has been shown that the 95 kDa B-Raf kinase is expressed in SH-SY5Y cells (Stephens et al. 1992). However, it is still unclear how cAMP activates B-Raf (Dumaz and Marais 2005). This may occur through activation of the cAMP-dependent Rap 1 GEF, Epac, or through another mechanism that may be potentiated by Epac (Lin et al. 2003) but may or may not involve Rap1 (Dumaz and Marais 2005). An additional possibility is the cAMP-mediated activation of PP2A (Feschenko et al. 2002) may directly induce B-Raf activation (Strack 2002). Activated ERK is required for neuritogenesis as well as being involved in the up-regulated expression of GAP-43, possibly through translocation to the nucleus. cAMP mediates the activation of p38 MAP kinase through a non-canonical pathway that may be similar to that observed in Th2 cells (Chen et al. 2000) and in cardiac fibroblasts (Yin et al. 2006), and which also may involve PP2A (Boudreau et al. 2004). Activated p38 MAP kinase in turn is involved in the increased expression of Bcl-2, possibly through phosphorylating CREB (Yin et al. 2006) and/or other factors, as well as in neuritogenesis. The arrows indicate direct interactions, the dotted arrows translocation, and the dot dash arrows the possibility of one or a number of intermediary steps that have not been worked out.