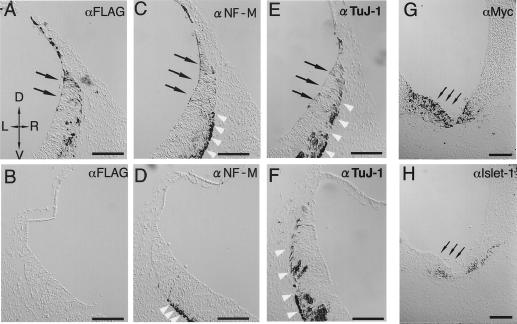
Figure 4.
Misexpression of Hu and Hu-R3 mutants in mouse embryonic CNS. Twelve-micrometer frozen serial sections of a HuC (FLAG-tagged)-transfected E9.5 mouse embryo (A–F) and a HuC-R3 (Myc-tagged)-transfected embryo (G and H) (D, dorsal; V, ventral; L, left; R, right). Sections of the HuC-introduced embryo were immunostained with antibodies against FLAG (A and B), neurofilament M (C and D) and TuJ-1 (E and F). Paired images of each individual section are shown from the transfected (A, C, and E) and nontransfected (B, D, and F) sides of the same slices. At the rhombencephalon of the normal mouse embryos in these stages (E9.5), the neurogenesis has already begun and neuronal markers are seen. Therefore, even in the nontransfected side (D and F), the expressions of authentic neuronal markers [TuJ1 (D); NF-M (F)] were observed in the outside of the ventricular zone (indicated by white arrowheads), corresponding to normal neuronal development. In the transfected side (C and E), however, ectopically induced expressions of neuronal markers were observed from within the ventricular zone [indicated by black arrows, TuJ-1 (C); NF-M (E)], coinciding with the expression of transfected FLAG-HuC [indicated by black arrows in (A)]. Such ectopic expressions of neuronal markers are never seen in normal neuronal development. Sections of a HuC-R3-transfected embryo were immunostained by using antibodies against Myc-tag (G) and Islet-1 (H). Islet-1-positive cells decreased in the HuC-R3 overexpressing region (indicated by small arrows). (Bar = 100 μm.)