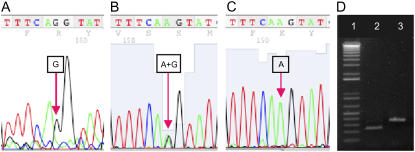
Figure 1.
BIO1 gene identification and nature of the point mutation in bio1-1. The 3′ end of the last intron of At5g57590 in wild-type plants (TTTCAG) is modified in bio1-1 homozygotes (TTTCAA). The 5′ end of the last exon (GTAT) remains unchanged. Refer to Supplemental Figure S1 for additional details on the location of this sequence polymorphism. A, Sequencing of genomic DNA from wild-type plants reveals a G nucleotide at the mutation site. B, Genomic DNA from heterozygotes yields a doublet peak that results from the expected mixture of A and G nucleotides at the mutation site. C, Rescued homozygotes exhibit a single peak, consistent with the G to A substitution. D, RT-PCR products obtained from this region demonstrate that transcripts from rescued homozygotes (lane 3) are longer than normal because they include the final intron (confirmed by sequencing) not found in transcripts from wild-type plants (lane 2). The five smallest bands in the DNA ladder (lane 1) range from 100 to 500 nucleotides.