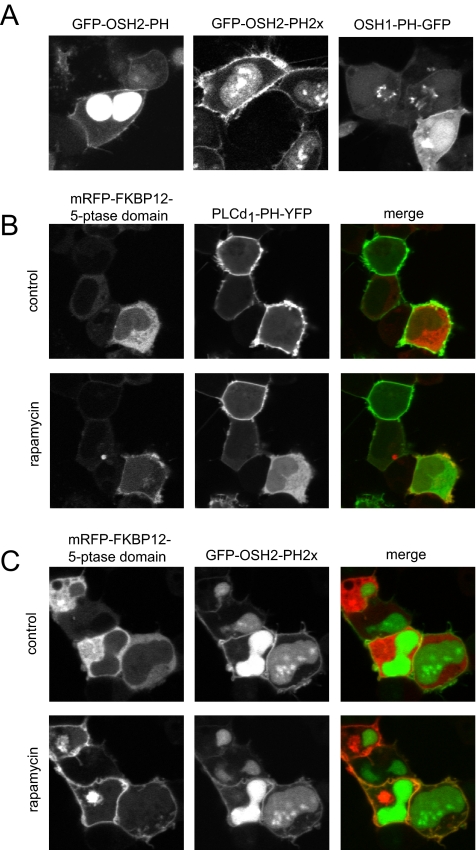
Figure 4.
Localization of OSH1- and OSH2-PH domain-GFP fusion proteins in HEK-293-AT1 cells. (A) The PH domains of the yeast oxysterol-binding protein homologues OSH2 and OSH1 were fused to GFP as described under Materials and Methods. These constructs were transfected into HEK-293-AT1 cells and examined 24 h after transfection with live cell confocal microscopy. Note that the OSH2-PH domain binds to the plasma membrane and strongly accumulates in the nucleus but does not bind to the Golgi. A tandem PH domain of the OSH2 protein shows smaller signal in the nucleus and a strong plasma membrane binding. The OSH1-PH domain binds both the plasma membrane and the Golgi. (B) Elimination of the plasma membrane localization of PLCδ1PH-GFP [monitoring PtdIns(4,5)P2] by plasma membrane recruitment of a phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase. HEK-293-AT1 cells were transfected with a truncated type-IV phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase fused to mRFP and FKBP12, a plasma membrane-targeted FRB-CFP construct and the PLCδ1PH-YFP reporter described in Varnai et al. (2006). Addition of rapamycin for 3 min recruits the otherwise cytoplasmic 5-ptase construct to the plasma membrane (left) with a concomitant elimination of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and loss of PLCδ1PH-YFP localization (middle). (C) The same manipulations do not eliminate the plasma membrane localization of the OSH2-PH2x-GFP, suggesting that this construct is not kept at the membrane by PtdIns(4,5)P2.