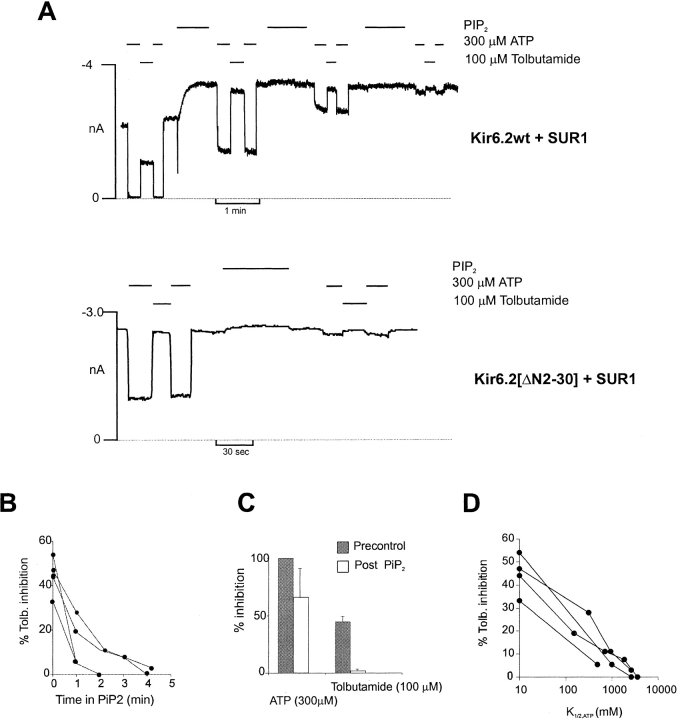
Figure 2.
Pip2 abolishes high-affinity tolbutamide inhibition of Kir6.2+SUR1 channels. (A) Representative currents from inside-out patches containing wild-type (Kir6.2+SUR1) or Kir6.2 [ΔN2-30]+SUR1 channels. The patches were exposed to [tolbutamide], [ATP], or [Pip2] as indicated. The dashed line indicates zero current (determined in 5 mM ATP). (B) Percent tolbutamide inhibition versus time in Pip2 for four individual patches containing wild-type KATP channels. (C) Percent inhibition by ATP or tolbutamide before (Precontrol) or after (Post Pip2) application of Pip2 (2–4 min) from patches in B. (D) Plot of the change in percent tolbutamide inhibition versus change in K 1/2,ATP after application of Pip2 for patches from B.