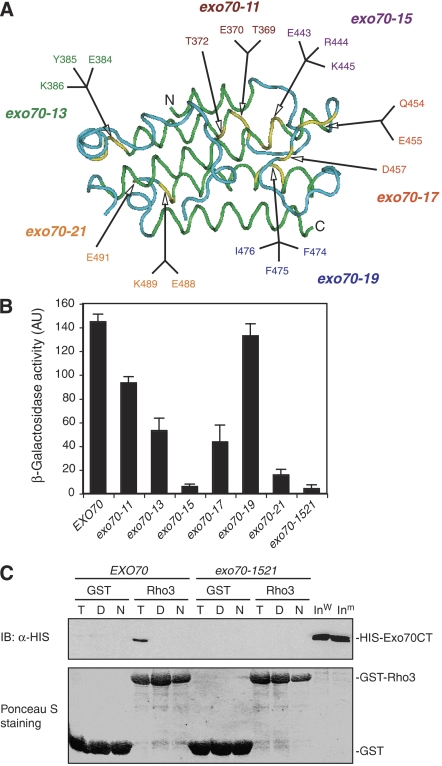
Figure 8.
Identification of Exo70 Domain C mutations that affect Rho3–Exo70 interaction. (A) The structure of Domain C of Exo70 that interacts with Rho3. The green and blue colors specify α-helices and loop regions in this domain. The yellow color indicates the residues mutated to alanine. (B) Yeast two-hybrid assay of the interactions between Exo70 Domain C mutants and Rho3. The average and s.d. of β-galactosidase activities were determined from three independent experiments. ‘AU', arbitrary units (n=3). (C) In vitro binding between the Exo70 Domain C mutant (exo70-1521) and Rho3. The C-termini (aa 358–623) of wild-type Exo70 and exo70-1521 (combining the mutations in both exo70-15 and exo70-21) were expressed as HISx6-tagged fusion proteins. Rho3 was expressed as a GST fusion protein and conjugated to glutathione Sepharose. These proteins were used in the in vitro binding assay in the absence of nucleotides (‘N') or in the presence of 0.05 mM GTPγS (‘T') or GDP (‘D'). GST (as control) and the GST-Rho3 fusion proteins used in the binding assay were stained by Ponceau S (lower panel). The Exo70 fusion proteins bound to GST-Rho3 glutathione Sepharose were detected by immunoblot (‘IB') using anti-HISx6 antibody. GST conjugated to glutathione Sepharose was used as a negative control in the binding reaction. ‘Inw', wild-type Exo70 input; ‘Inm', mutant Exo70 input.