Figure 4. Effect of external zinc on the sodium dependence of the glutamate uptake current.
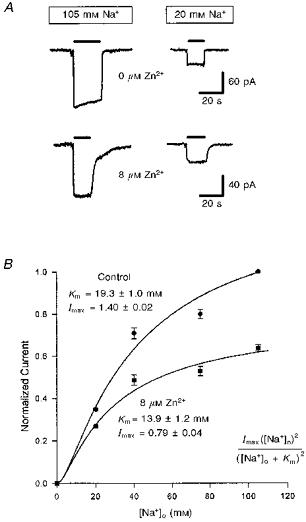
A, specimen data showing the effect of 8 μm free zinc on currents evoked at −60 mV by 200 μm free glutamate (filled bars) in normal solution (105 mm Na+, left traces) or in solution containing only 20 mm Na+ (replaced with choline, right traces). Data in zinc have been normalized (note different current scales) so that the response in 105 mm Na+ is the same as in control solution, to facilitate comparison of the relative sizes of response in 20 mm Na+. External solution was the 105 mm sodium solution described in the Methods. B, dependence of the glutamate-evoked current on external sodium concentration for 5 cells in solutions lacking zinc (circles) and containing 8 μm zinc (squares). Data are normalized to the response in normal solution with 105 mm [Na+]o. Smooth curves are the square of a Michaelis-Menten equation (inset) best fitted to the data. Imax is the normalized current predicted at a saturating sodium concentration; Km is the sodium concentration at which the normalized current is quarter-maximal.
