Figure 6. Effect of zinc on glutamate uptake at different external pH values.
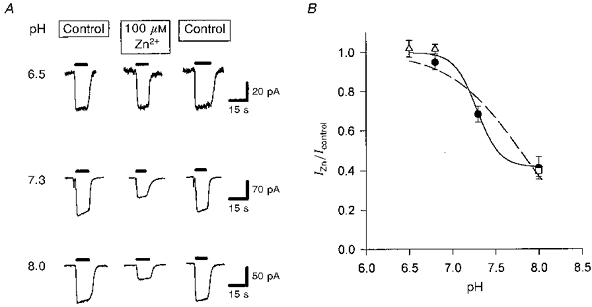
A, specimen data showing currents evoked at −60 mV by 200 μm glutamate (filled bars) in control solution, in solution containing 100 μm free zinc, and again in control solution (data from a different cell for each pH value). Experiments were done using gluconate-containing solutions (see Methods) to avoid any contamination from current generated by the anion channel in the glutamate transporters. B, mean data from experiments like that in A on 4 cells (except 3 cells for pH 6.5 and 10 cells for pH 7.3), showing the suppression by zinc of the uptake current as a function of pH. Filled circles, Hepes used as a pH buffer. Open triangles and open square, 5 mm Taps and Mes, respectively, used as a pH buffer. The fitted curves have the form: IZn/Icontrol =A+[(1 - A)HN/(HN+KN)], with H =[H+] and constants A = 0, K = 1.64 × 10−8 and n = 1.047 (dashed line; assumes response is completely suppressed by zinc at very alkaline pH), or A = 0.417, K = 5.18 × 10−8 and n = 3.36 (smooth line; allows response to be incompletely suppressed by zinc at very alkaline pH).
