Figure 8. Simulated effects of RB neuron stimulation on interneurons.
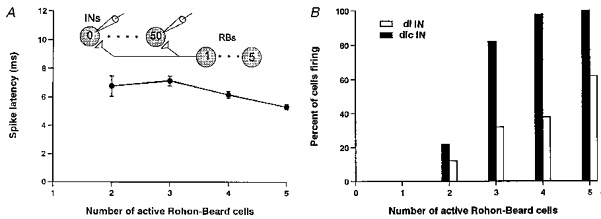
The effect of the number of model RB neurons stimulated on a population of 50 model dlc interneurons with variation in RB conduction times, RB to interneuron synaptic conductances and interneuron soma areas (specific capacitance, 0.009 F m−2; specific conductance, 9 S m−2). A, interneuron spike latencies still decrease with the number of RB neurons stimulated. B, when the synapses from RBs to dl interneurons are half the conductance of those to dlc interneurons, fewer dl interneurons are recruited but recruitment of the two populations of interneurons occurs over a sensible range.
