Figure 8. ENO-associated barrages of synaptic currents are carried predominantly by chloride ions.
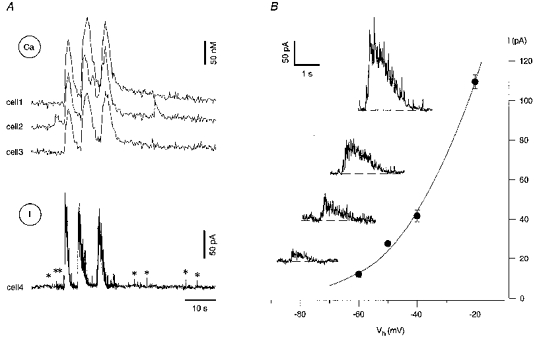
A, [Ca2+]i measurements from 3 fura-2 AM-loaded pyramidal neurones (Ca, cells 1-3) combined with the whole-cell current recording from a neighbouring pyramidal neurone (I, cell 4) voltage clamped at -20 mV. The pipette solution contained only 2 mM Cl− to obtain a reversal potential for Cl− at -109 mV (see Methods). Note that both the ENO-associated slow currents and the spontaneous synaptic currents (asterisks) detected before and after the burst were outward. B, current-voltage relation of the ENO-associated currents recorded in the voltage-clamped cell 4. The amplitude of the current represents the mean value within a 200 ms window at the peak of the response. Each point represents a mean of 3-8 measurements. The slice was obtained from a rat at P2. Insets illustrate ENO-associated currents recorded (from top to bottom) at holding potentials (Vh) of -20, -40, -50 and -60 mV.
