Figure 6. Effect of hypoxia on the depolarizations of an inspiratory neurone in a P12 mouse.
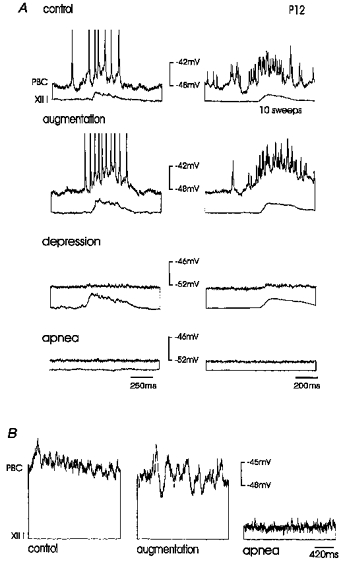
A, the rhythmic drive potentials occurring in phase with integrated XII activity were suppressed during depression (third panel) and abolished during apnoea (fourth panel). Left panels, original recording. Right panels, recordings averaged from ten sweeps. B, the membrane potential recorded during the interburst intervals was compared with control conditions (left panel) characterized by increased synaptic noise during augmentation (middle panel), followed by a decreased level of synaptic activity during apnoea (right panel).
