Figure 5. Effects of exposure to 100 nM insulin for 5–9 h on K+ currents in myocytes from STZ-treated rats.
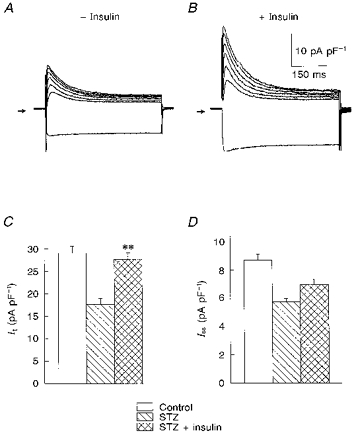
A and B, superimposed current traces in response to voltage steps (as in Fig. 1) in two myocytes obtained from a STZ-treated rat, with no insulin added (A), and following 6 h in insulin (B). The currents were divided by the cell capacitances, so that densities can be compared. It was greatly enhanced, with little effect on the steady-state amplitude at the end of the pulse. C and D, summary data (means ± s.e.m.) of current densities (at +50 mV) in cells (n = 34) from control rats, and from STZ-treated rats, in the absence (n = 29) or presence (n = 36) of insulin. The enhancement of It was statistically significant (** P < 0.001, STZ + insulin vs. STZ), whereas Iss showed a tendency to increase which did not achieve statistical significance.
