Figure 6. Effect of nifedipine on 20-HETE-induced activation of macroscopic Ca2+ current carried by Ba2+ and constriction of isolated cerebral arterial segments.
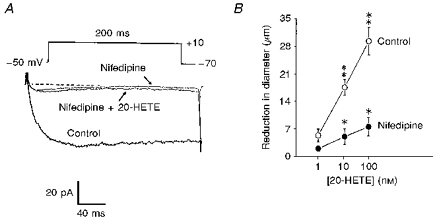
A, nifedipine (2 μm) applied to the bath abolished the macroscopic Ca2+ current elicited by a 200 ms depolarizing pulse from a holding potential of −70 mV to a test potential from −50 to +10 mV. Addition of 100 nm 20-HETE in the presence of nifedipine failed to enhance the macroscopic Ca2+ current (n = 6). B, effect of nifedipine (2 μm) on the 20-HETE-induced concentration-related constriction of isolated pressurized (90 mmHg) cat cerebral arterial segments. Nifedipine significantly depressed the 20-HETE-induced constriction of the arterial segments at all concentrations studied. Vertical bars denote s.e.m. Single asterisks represent significant differences in the concentration-related contractile effects of 20-HETE before and after application of nifedipine. Double asterisks represent significant differences between the contractile effects of low and high concentrations of 20-HETE studied under control conditions (n = 5, P < 0.05).
