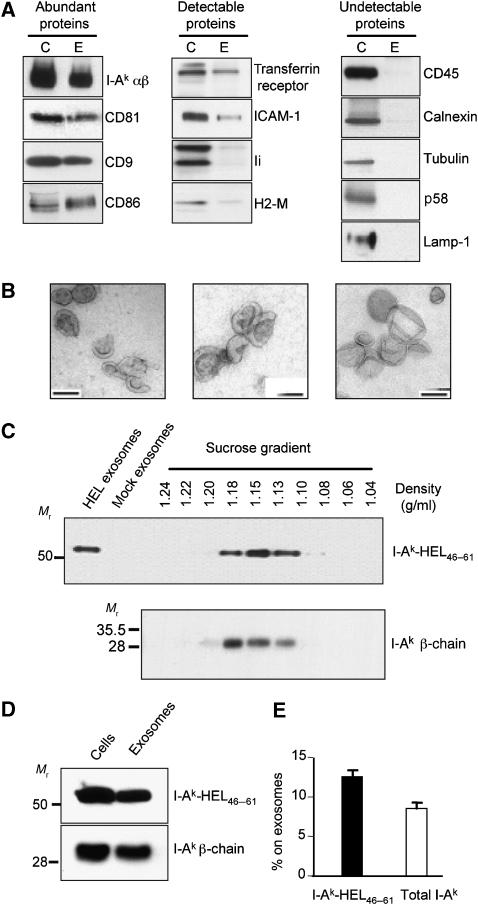
Figure 1.
B cells secrete 12% of their I-Ak-HEL46–61 complexes on exosomes in 24 h. (A) Exosomes were isolated from LK35.2 B cells. The exosome-donor B cells (C) were lysed, and the exosomes (E) were concentrated 10-fold relative to the volume of the B cell lysate. Equal proportions of B cell lysate and exosome lysate were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting to detect the indicated proteins. pMHC-II complexes were detected by incubating lysates with SDS–PAGE sample buffer at room temperature. The proteins analyzed were sorted into the following three categories: (i) those relatively abundant in exosomes, (ii) those detectable at low levels in exosomes, and (iii) those undetectable in exosomes. (B) Electron microscopic analysis of exosome preparations obtained by differential centrifugation from supernatants of LK35.2 cells. Bars, 100 nm. (C) LK35.2 cells were cultured in medium alone or medium containing 1 mg/ml HEL protein for 24 h. Equivalent portions of exosomes isolated from cells incubated with HEL (HEL-exosomes) or in medium alone (mock exosomes) as well as aliquots of each sucrose density gradient centrifugation fraction were analyzed by SDS–PAGE under non-boiling conditions and immunoblot analysis using mAb C4H3 to detect SDS-stable I-Ak-HEL46–61 complexes. The density of each fraction was determined using a refractometer and is shown above each fraction. (D, E) The exosome pellet obtained after differential centrifugation was concentrated 10-fold relative to that of the B cell lysate. The proportion of I-Ak-HEL46−61 complexes (determined by immunoblotting non-boiled samples with mAb C4H3) or total I-Ak β-chain (determined by immunoblotting boiled samples with an anti-I-Ak β-chain antibody) secreted on exosomes was expressed as a percentage of the total amount of immunoreactivity recovered on exosomes and cells. The graph shows the average±s.d. of data from five independent experiments.