Figure 3. Velocity dependence of the various tension components in a slow-twitch muscle fibre bundle before (triangles) and after (circles) chemical skinning.
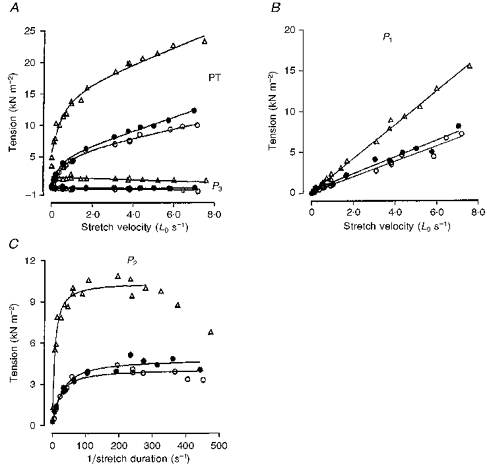
The data are presented in the same way as in Fig. 2B, C and D. In this preparation P1 tension analysis gives a viscosity coefficient of 2.05 kN s m−2 (per Lo) before skinning and 0.93 kN s m−2 (per Lo) after chemical skinning. The curve fitted to P2 tension has a relaxation time of 48 ms in the intact fibre and 29.6 ms after chemical skinning. •, data from the skinned preparation obtained in the presence of 4 % dextran in the relaxing solution. Note that chemical skinning reduces the tension amplitude at all velocities and that the addition of 4 % dextran improves the amplitudes only marginally.
