Figure 8. Pyrophosphate fails to stimulate murine CFTR Cl− channels.
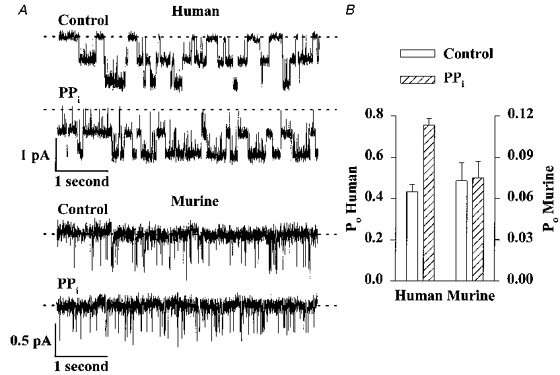
A, effect of PPi (5 mM) on the activity of two human and two murine CFTR Cl− channels. ATP (0.3 mM) and PKA (75 nM) were continuously present in the intracellular solution; voltage was -50 mV. Each trace is 5 s long. B, effect of PPi (5 mM) on the Po of human (left ordinate) and murine (right ordinate) CFTR Cl− channels. Note the change in scale. Columns and error bars indicate means +s.e.m. of n = 4 and n = 6 for human and murine CFTR, respectively. PPi (5 mM) increased the Po of human CFTR to 175 ± 8% of the control value (n = 4; P < 0.01), but was without effect on the Po of murine CFTR (n = 6; P > 0.05). Other details as in A. Using the conditions described, PPi (5 mM) increased the Po of human CFTR Cl− channels in membrane patches excised from CHO cells expressing wild-type human CFTR to 0.82 ± 0.13 (mean ±s.d.; n = 2; 189 ± 6% of the control value; n = 2).
