Figure 8. The effects of NA on Ip are eliminated by prazosin (Pz), a specific α1-antagonist, but unaffected by yohimbine (Yo), a specific α2-antagonist.
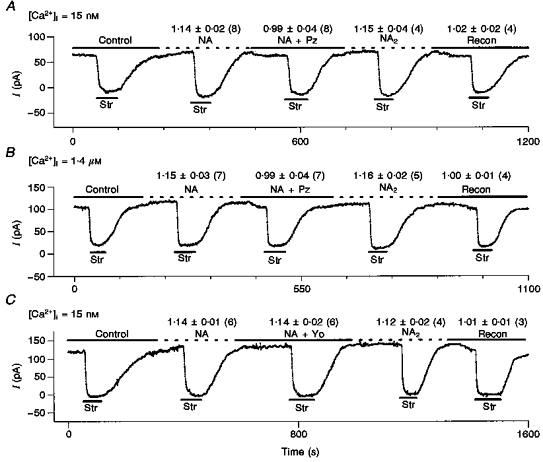
Above each test condition, we report: mean Ip(test)/Ip(con)±s.d. (number of cells). A, a typical record in low (15 nm) [Ca2+]i. We measured control Ip(con), applied 10 μm NA and measured Ip(NA), added 10 μm prazosin to the NA-containing solution and measured Ip(NA+Pz), washed out the prazosin and remeasured Ip(NA2), and lastly washed out the NA and remeasured control Ip(recon), In all experiments reported, we measured Ip(con), Ip(NA) and IP(NA+Pz), but in half of these we lost the patch before obtaining our second measurements Ip(NA2) and Ip(recon). B, the same protocol and information are illustrated except [Ca2+]i was 1.4 μm and NA was 1 μm. C, the protocol is the same as in A, except the α2-antagonist yohimbine (Yo) is substituted for Pz. However, 1 μm Yo does not antagonize the NA-mediated stimulation of Ip. These data provide direct evidence that the effects of NA on Ip in ventricle are mediated by the α1-receptor subtype. Moreover, in the 13 cells in which we were able to record Ip(NA2)/Ip(con), the ratio is within 1 % of the initial Ip(NA)/Ip(con), and in the 11 cells in which we completed the protocol, Ip(recon) is within 2 % of the initial Ip(con). Thus, our measurement of the NA effect is reproducible and run-down of Ip is negligible.
