Figure 1. Properties of extracellularly recorded TC neurones and power spectra of the EEG in immobilized GAERS.
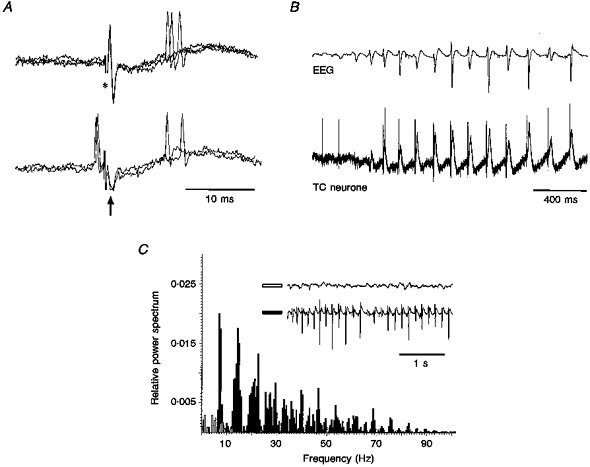
A, orthodromic response of a TC neurone (top, 3 superimposed traces) to stimulation of the sensory motor cortex (*), and collision test (bottom, 3 superimposed traces) (arrow indicates the antidromic field potential). Note the failure of an antidromic response due to collision with a spontaneous action potential. B, extracellular recordings (bottom trace) from the same unit as in A show the action potential firing to become time-locked with the spike component of the spike-wave complex in the EEG (top trace). Note the large field potential occurring in close time relationship with the EEG spike-wave complex. C, EEG power spectra before (open bars) and during (filled bars) a SWD show the marked increase in power during, and the shift towards the dominant frequency (6-9 Hz) of, spike-wave complexes. Note the change in the amplitude of the spike-wave complexes throughout a SWD.
