Figure 1. Assessment of the rate of action of Streptomyces hyaluronidase on synovial hydraulic permeability.
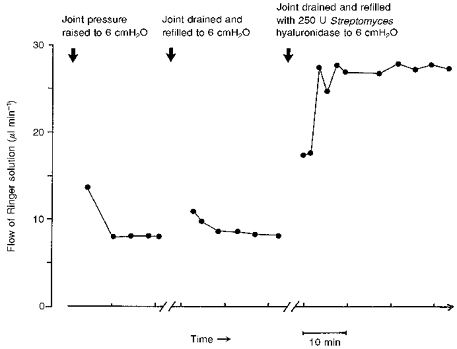
The first group of points shows the inflow of Ringer solution into the cavity of the rabbit knee from the infusion reservoir after a step rise in infusion pressure. The initial high inflow is due to joint expansion as intra-articular pressure rises to its new set level. After pressure in the joint has stabilized (here at 6 cmH2O) inflow settles to a steady rate that reflects rate of fluid absorption across the synovial lining. Aspiration and refilling with Ringer solution did not significantly change the steady state absorption rate (second curve). Aspiration and refilling with Ringer solution containing 250 U Streptomyces hyaluronidase increased the absorption rate 3.5-fold within 3 min of the first measurement, with no further rise over 30 min (third curve). The first measurement was several minutes after enzyme injection due to the time needed to re-establish control pressure (interrupted time axis).
