Figure 2. α-BgTx inhibition of ACh-evoked currents was direct and independent of Ca2+-induced Cl− conductance.
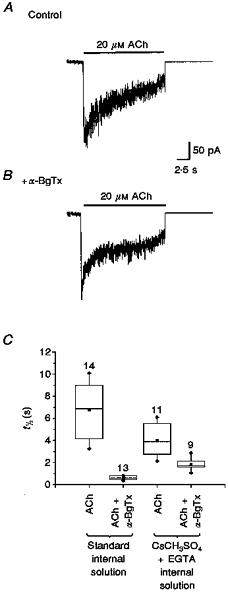
ACh (20 μM)-evoked macroscopic currents in the presence or absence of α-BgTx (500 nM) were recorded with CsCH3SO4+ high EGTA internal solution (see Methods). The recorded currents were digitized, averaged and analysed. A, averaged currents evoked by ACh (20 μM) in neurones using CsCH3SO4 internal solution. B, averaged currents evoked by ACh +α-BgTx under the same conditions as in A. The time course of the current decay was faster than that recorded with standard internal solution. C, the t½ values of the decay phase of the currents were analysed with non-parametric methods and presented as box plots (see Methods). Comparison of t½ of all ACh (20 μM)-evoked currents in the absence or presence of α-BgTx recorded under control conditions in standard internal solution or in CsCH3SO4+ EGTA internal solution revealed significant (P≤ 0.001) inhibition of ACh-evoked currents by α-BgTx whether or not Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance was blocked. The number of neurones recorded are noted above each box plot.
