Figure 2. H-7 does not prevent leptin activation of KATP channels.
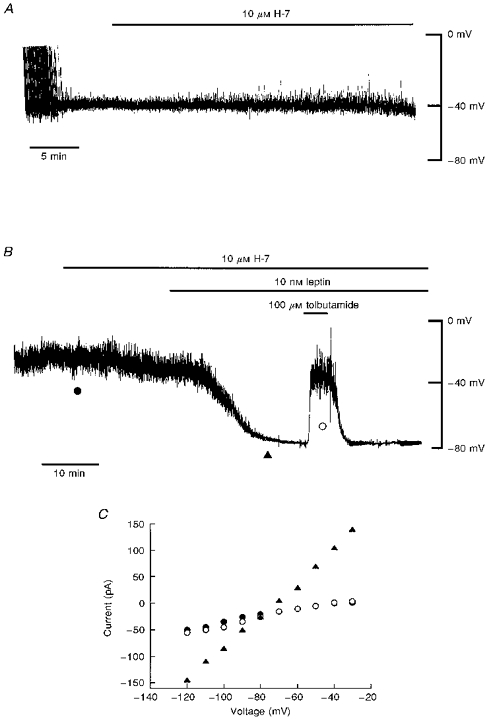
A, current clamp record of a cell dialysed with an electrode solution containing 5 mM ATP. Addition of H-7 (10 μM) for approximately 20 min (as indicated by the bar) had no effect on the resting membrane potential of CRI-G1 cells. B, current clamp record of a cell dialysed with 5 mM ATP-containing electrode solution. Application of H-7 (10 μM) for the time indicated had no effect on the resting membrane potential. Addition of leptin (10 nM) 10-15 min after prior exposure to H-7 (10 μM) resulted in hyperpolarization of CRI-G1 cells from -40 to −78 mV. Tolbutamide (100 μM) applied after the leptin-induced hyperpolarization caused complete reversal of the membrane potential to pre-leptin levels. C, plot of the current-voltage relationships for the voltage clamped currents obtained at the points specified in B: •, H-7; ▴, leptin and H-7; ○, tolbutamide. H-7 (10 μM) did not prevent the leptin-induced increase in K+ conductance.
