Figure 4. The effects of phentolamine, guanethidine, α,β-methylene ATP and tetrodotoxin on the rapid EJPs recorded from choroidal arterioles.
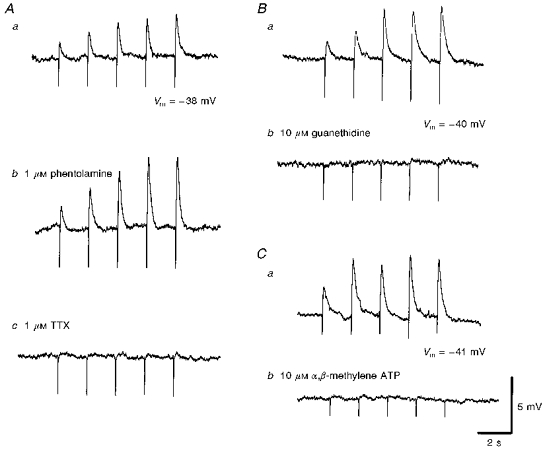
The rapid EJPs evoked by trains of stimuli (supramaximal voltage, 50 μs, 0.5 Hz, 10 s; Aa) in choroidal arterioles persisted in the presence of phentolamine (1 μM; Ab) but were abolished by tetrodotoxin (TTX, 1 μM; Ac). EJPs were abolished by guanethidine (10 μM; Bb) and by α,β-methylene-ATP (10 μM; Cb). A, B and C were recorded from 3 different cells. Aa, Ba and Ca are respective control responses. In each trace, the small downward deflection at the beginning of each EJP indicates the artefact of nerve stimulation. The scale bars on the right refer to all traces. Vm refers to resting membrane potential.
