Figure 5. The effects of phentolamine and guanethidine on slow depolarizations recorded from choroidal arterioles.
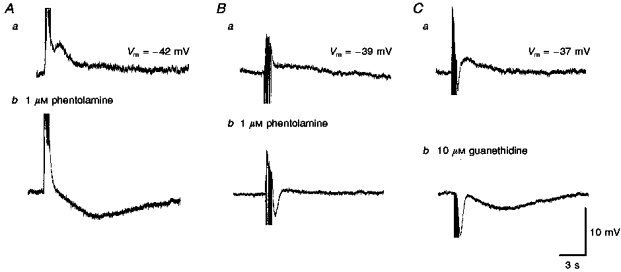
The slow depolarizations evoked by trains of stimuli in two different preparations (supramaximal voltage, 50 μs, 10 Hz, 1 s; Aa and Ba) were abolished by phentolamine (Ab and Bb). In both preparations, the initial purinergic responses persisted. In one of the preparations a slow hyperpolarization was revealed (Ab); in the other a rapid IJP was detected (Bb). In the third preparation both the purinergic and slow depolarization evoked by a train of stimuli (supramaximal voltage, 50 μs, 50 Hz, 1 s, Ca) were abolished by guanethidine to reveal a slow hyperpolarization and an augmented IJP (Cb). A, B and C were recorded from 3 different cells. The scale bars on the right refer to all traces. Vm refers to resting membrane potential.
